1 Objective
The objective of this chapter is to give a brief overview of the accounting life cycle and relevant guidance on the accounting treatment of revenue arising from exchange transactions within the Umoja environment. Accounting of revenue from exchange transactions is primarily housed within the Sales and Distribution module of Umoja.
This chapter details how an end user, based on the involved Umoja user profiles, should perform roles and responsibilities related to accounting of revenue from exchange transactions.
This chapter is based on guidance under IPSAS 9: Revenue from Exchange Transactions, which focuses on determining when to recognize revenue and the appropriate amount of revenue to be recognized from exchange transactions.
2 Summary of IPSAS Accounting Policies
2.1 Introduction to Goods and Services
Goods include (a) goods produced by the entity for the purpose of sale, and (b) goods purchased for resale, such as merchandize. Goods are typically sold as standard orders; however stamps and publications can be sold on consignment.
The rendering of services typically involves the performance by the entity of an agreed task over an agreed period of time. The service may be rendered within a single period or over more than one period.
The following items fall into the UN's scope of revenue from exchange transactions:
· United Nations Postal Administration (UNPA)
· Guided tours, lectures and briefings, seminars and special events
· Sale of UN publications
· Sale of statistical reports and demographic-related products
· Sale of gift items
· Garage operations
· Newsstand operations
· Food services and catering operations
· Accommodations and lodging
· Other self-sustaining commercial activities
· Third party procurement
The following items will be addressed in other chapters of the Finance Manual:
· Rentals (refer to Finance Manual Chapter on Leases)
· Sale of property, plant and equipment/inventory (refer to Finance Manual Chapters on Property, Plant and Equipment and Inventory)
2.2 Recognition of Revenue
Revenue is recognized when it is probable (probability greater than 50%) that (a) future economic benefits or service potential will flow to the UN; and (b) these benefits can be measured reliably. No revenue is recognized unless these two primary conditions are met. Specifically, revenue from the sale of goods is recognized when significant risks and rewards have been transferred, the UN neither retains continuing managerial involvement or effective control over the goods and cost incurred can be reliably measured.
Revenue from the provision of services is recognized in the financial period in which the service is rendered according to the estimated stage of completion of that service, provided that the outcome can be estimated reliably (i.e. if the stage of completion of the transaction at the reporting date, costs incurred and costs necessary to complete the transaction can be measured reliably). Therefore, revenue from tours will be recognized in the financial period in which the tour was given. When the outcome of the transaction involving the rendering of services cannot be estimated reliably, revenue shall be recognized only to the extent of the expenses recognized that are recoverable.
2.3 Measurement of Revenue
Revenue shall be measured at the fair value of the consideration received or receivable.
The amount of revenue arising on a transaction is usually determined by an agreement between the UN and the purchaser or user of the asset or service. It is measured net of any trade discounts and volume rebates allowed by the UN. When the inflow of cash or cash equivalents is deferred beyond 12 months, the fair value of the consideration may be less than the nominal amount of the transaction due to inbuilt interest component. Note: Discounting is determined to be immaterial in the UN context.
2.4 References
For more details on the IPSAS requirements regarding revenue from exchange transactions, refer to:
· The UN IPSAS Policy Framework
· IPSAS 9 - Revenue from Exchange Transactions
3 Revenue from Exchange Transactions covered in the Sales and Distribution Module
3.1 Sales and Distribution Module Overview
The majority of the UN's commercial operations i.e. exchange revenue transactions are covered in the Sales and Distribution module (SD) of Umoja. SD is the supply chain and sales order processing module in Umoja.
There are four (4) areas covered by the SD module:
· Pre-sales activities
· Sales order processing
· Shipping
· Billing, including billing document and invoice creation
The SD module is integrated with other modules/sub modules including Master Data, Supplier Relationship Management (SRM), Financial Accounting and Business Intelligence (BI). This allows for eased communication between the modules/sub modules.
3.2 Sale of Goods or Rendering of Services Lifecycle
The sale of goods or rendering of services lifecycle typically involves the creation of a pricing record and the sale of the goods or services through various outlets. After the sale has occurred, goods can be returned or a credit/debit memo can be created.
Garage and accommodation processing do not follow the typical sales processes described in the sales process section, and thus are included in a separate 'special cases' category.
3.2.1 Pricing and Discount Process
The Pricing process includes determining product or service list price, customer discounts, trade discounts and shipping charges. Once these pricing elements are finalized, pricing records will be created in the system for the product or service. The master records will then be used during Sales Order Processing.
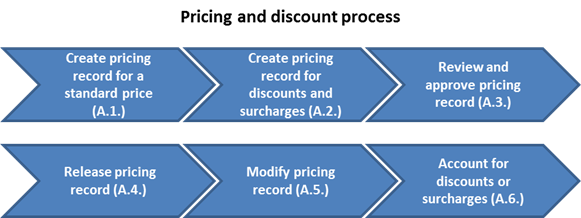
A. The following process steps are applicable to pricing:
A.1. Create pricing record for the standard price / Transaction Code: VK31 or VK11
The Price Maintainer of a commercial operation is responsible for creating the pricing record for the product list price in the system.
A.2. Create pricing record for discounts and surcharges / Transaction Code: VK31 or VK11
If there are any discounts/surcharges that apply, the Price Maintainer will create the pricing record for discounts and surcharges in the system.
There are several scenarios of discounts and surcharges which are listed below:
• Staff Member Discount
• Discount for Developing and Least Developed Countries
• Trading Discount
• Promotion Discount
• Shipping and Freight Charges: There are two (2) types of shipping and freight charges:
o UNPA and the Bookshop charge shipping and handling for sales orders and this will be created as a pricing record using a percentage rate based on the product list price or a scaled fix price based on the order value
o Freight cost needs to be charged based on the delivery country and receiving country. This will be created as a different pricing record.
· Administrative fee as a percentage or value
A.3. Review and approve the pricing record
Based on enterprise roles assigned in iNeed and their authority, the pricing request (for standard and discount/surcharge pricing) is routed to the appropriate approver for review and approval of the new or updated pricing request.
A.4. Release pricing record
If approved, the request is sent to the Price Maintainer, thus releasing the pricing record so the new price will be effective. (The product cost is captured in the system within the material master record.)
A.5. Modify price record / Transaction Code: VK32 or VK12
If the pricing record is not approved, then the Requester will modify or clarify the price request accordingly. The process will start from step one.
A.6. Accounting for discounts / surcharges
If a discount (e.g. discount of USD 10) is applied to a sale of a publication to a commercial customer, the recognition of the receivable will be processed in the background processing as follows:
|
Date |
GL |
GL short description |
Debit |
Credit |
|
2 Feb 2014 |
15101510 |
AR Exch Commercial Customer |
90 |
|
|
|
62811012 |
Sale IS3 PublicaDisc |
10 |
|
|
|
62811010 |
Sale IS3 Publication |
|
100 |
3.2.2 Sales Processes
Sales orders can be processed through five different methods: standard sales orders, over the counter sales, third party procurement, customer consignment and standing orders. Each method has different processes, which are discussed in detail in the following sections. The section begins with standard sales orders.
Please refer to UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for:
· 'Free of Charge Sales Order Processing' - page 92;
· 'Standard Order with Down Payment Processing' - page 98;
· 'Resource Related Billing (RRB) Order' - page 107.
Also, please refer to UMOJA Service and Maintenance Order Management User Guide for Service Order Processing.
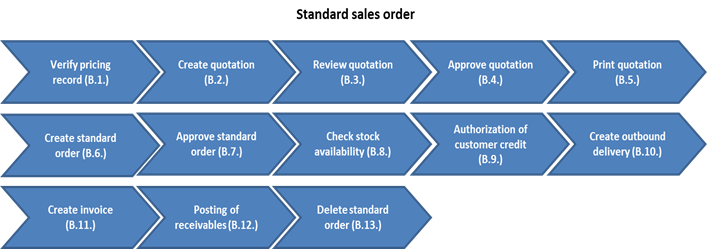
3.2.2.1 Standard Sales Order
The sales order processing in SAP is designed to support standard sales cycles. A centralized order management system will provide visibility into the order status, stock level and financial accounting data. Standard orders begin with the quoting process, followed by the creation of a standard order, an outbound delivery and finally an invoice. The system will automatically generate the posting of the receivable. Standard orders can be created in reference to the customer quotation or created independently without reference and can be used for sales of goods and services.
Please refer to UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for:
· 'Display/Change quotation' - page 30;
· 'Display/Change sales order' - page 65.
B. The following steps are applicable to the standard sales order process:
B.1. Verify pricing record / Transaction Code: VK13
B.1.1. Type VK13 in the Command field and click the Enter icon.
B.1.2. Click the Matchcode icon in the Condition type field to open the search feature for the condition type.
B.1.3. Select the appropriate condition type from the displayed list and click the Continue icon.
Please refer to picture 'Restrictions' in step 4 on page 27 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.1.4. Click the Enter icon.
B.1.5. The Key Combination window is displayed. Select the radio button for the appropriate key combination. Click the Continue icon.
Please refer to picture 'Create Condition Records' of step 7 on page 28 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
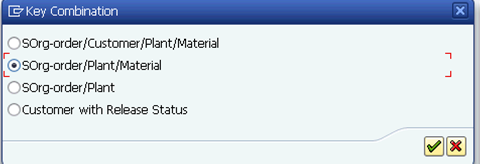
Note: The Key Combination determines how pricing conditions are used. For example, the key combination selected in the picture, signifies that the pricing conditions should apply on the Plant and Material level. The more criteria specified, the more specialized the pricing conditions become. Specific conditions always override general conditions.
B.1.6. Populate the relevant criteria for display, such as Sales org. of order, Plant, Material and Valid On fields. Click the Execute icon.
Please refer to picture 'Display CustAdminFee' of step 9 on page 28 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.1.7. Verify the following fields: Plant, Material, Amount, Approval Status, Valid to, Valid From.
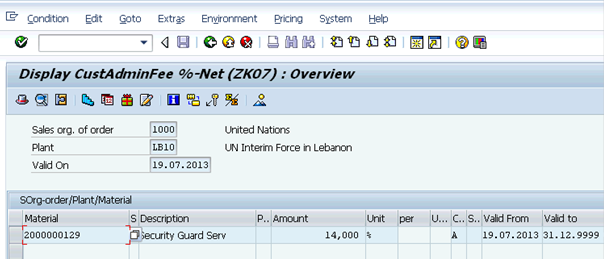
B.2. Create Quotation / Transaction Code: VA21
B.2.1. Type VA21 in the Command field and click the Enter icon.
B.2.2. Populate the following fields and click the Enter icon:
• Quotation Type (ZQ2 UN Quotation - Manual)
• Sales Organization (1000)
• Distribution Channel
• Division
• Sales Group [If the value is typed in (i.e. if the value is not picked from the dropdown list), enter the Sales Office as 0001- United Nations]
Please refer to picture 'Create Quotation: Initial Screen' of step 2 on page 31 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.2.3. Type the BP Number in the Sold-To Party field. The Ship-To Party field will be automatically populated.
B.2.4. Type the appropriate date in the Valid to field under the Sales tab.
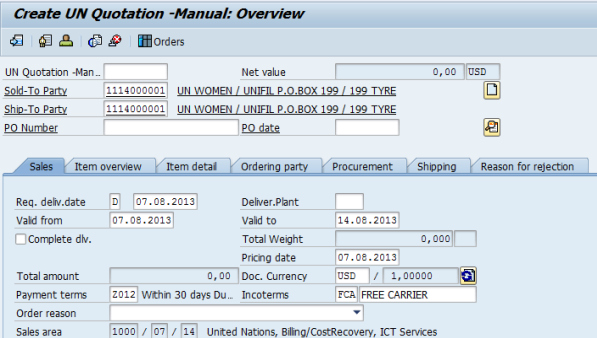
B.2.5. In the Sales tab, the SD User can type the appropriate information in the Material, Order Quantity, Amount, Currency and Plant fields. Check REQ - Approval Requested when complete to submit the relevant line item for approval by the SD Approver.
B.2.6. The SD User can click the Save icon and note the created Quotation number.
B.2.7. If additional information is required, a message box will appear. Choose Edit and the system will display all the fields that still need to be maintained (Note: The next steps are alternative/optional steps to maintain this information).
B.2.7.1. Alternatively, the SD User can enter the material number and then populate or amend the information contained in the quotation by selecting the material item and clicking the Display Item Details icon or double-clicking the line item.
B.2.7.2. At the item level, maintain or, if required, populate the Sales A and Sales B tabs.
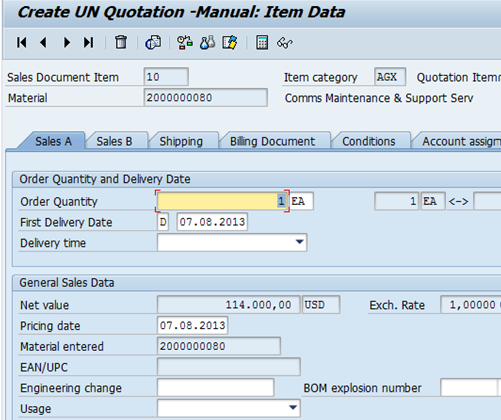
Please refer to second picture 'Create UN Quotation-Manual: Item Data' of step 8 on page 32 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration of Sales B tab.
B.2.7.3. Type the appropriate value for the mission or office responsible for delivering the service in the Plant field under the Shipping tab.
Please refer to picture 'Create Quotation - Manual: Item Data' of step 9 on page 33 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.2.7.4. Type the required data in the Terms of Payment field under the Billing Document tab.
Please refer to picture 'Create Quotation - Manual: Header Data' of step 10 on page 33 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.2.7.5. Under the Conditions tab, click the Matchcode icon in the CnTy field.
Please refer to picture 'Conditions Tab view' of step 11 on page 34 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.2.7.5.1. Select the Conditions Type from the displayed list. Note, in addition to the Condition Type 'PR00 - Price', other Condition Types can be added if they have not been automatically added through the Pricing Conditions Master such as:
• ZK09 - Ship and Handling Fee
• ZK07 - Customer Administrative Fee
• K007 - Customer Discount
• KF00 - Freight Surcharge
B.2.7.5.2. Click the Copy icon.
Please refer to picture 'Condition Type' of step 13 on page 34 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.2.7.5.3. Type the appropriate price in the Amount field and press Enter.
B.2.7.5.4. Verify that the Pricing Conditions applicable to the client have been applied (if any).
Please refer to picture 'Create Quotation - Manual: Item Data' of step 16 on page 35 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.2.7.6. Under the Status tab, click the Object Status button.
Please refer to picture 'Create Quotation - Manual: Item Data' of step 17 on page 35 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.2.7.7. Select the REQS Approval Request radio button and click the Back icon.
Please refer to step 18 on page 35 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for list of different statuses.
Please refer to picture 'Change Status' of step 19 on page 36 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.2.7.8. Click the Save icon.
B.2.7.9. Note the Quotation number for future reference.
Please refer to picture 'Create Quotation - Manual: Item Data' of step 21 on page 37 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
Please refer to page 37 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for Creating a Quotation with Reference to a Service Order - DP80.
B.3. Review quotation / Transaction Code: VA23
B.3.1. To review the quotation, either click the Sales document menu and select Display, or use transaction code VA23.
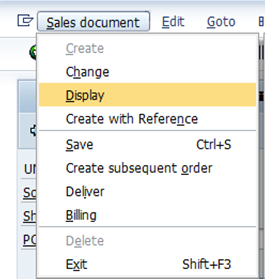
Please refer to page 40 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for Display / Change a Quotation - VA22 & VA23.
B.4. Approve the quotation / Transaction Code: V.26
B.4.1. The SD approver will type V.26 in the Command field and click the Enter icon.
B.4.2. Click the Variant icon and choose the variant UN Quotations Waiting for Approval. Press the Enter key on your keyboard.
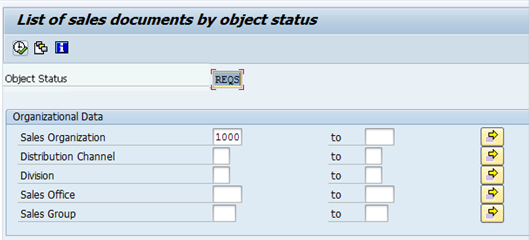
Please refer to picture 'List of sales documents by object status' of step 2 on page 47 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.4.3. Enter the relevant Sales Area to view quotations assigned to the Approver.
B.4.4. Click the Execute icon à a list of quotations pending approval will be displayed.
B.4.5. Double-click the relevant Quotation to be approved.
B.4.6. At the material line item level, change the status of all or relevant line items from REQS to APPR - Approved.
B.4.7. Click the Save icon.
B.5. Print the quotation / Transaction Code: VA22
B.5.1. After the quotation is approved, the SD User or SD Approver can print the Quotation by typing VA22 in the Command field and clicking the Enter icon.
B.5.2. Ensure that the SD User/SD Approver is in the Change mode and type the quotation number in the Quotation field. Click the Search button.
Please refer to picture 'Change Quotation: Initial Screen' of step 3 on page 50 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.5.3. Click the Extras menu and select Output > Header > Edit.
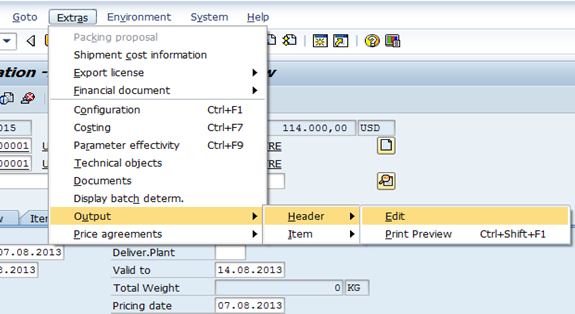
B.5.4. Type ZAN0 - UN Quotation in the Output field (or select from the drop-down menu) to print using the UN customized Sale Order format. Note that the Status field will indicate a triangle.
B.5.5. If the form needs to be printed in a language other than the defaulted language, go to the Language column and change to the required language code.
B.5.6. Click the Communication method button.
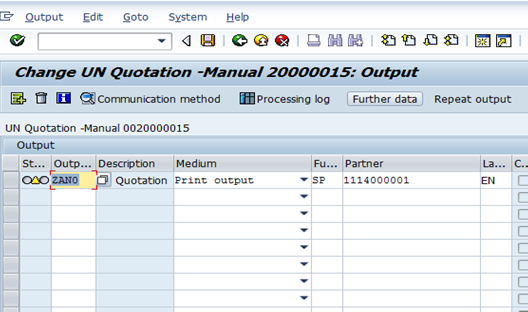
B.5.7. Type LOCL in the Logical destination field.

B.5.8. Select the Print immediately check box and click the Back icon.
B.5.9. Click the Further Data button.
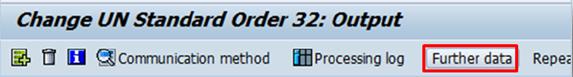
B.5.10. Select Send Immediately (when save the application) from the Dispatch time drop-down list and click the Back icon.
Please refer to picture 'Change Quotation - Manual 20000015: Output' of step 15 on page 52 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.5.11. Click the Save icon and note the system message.
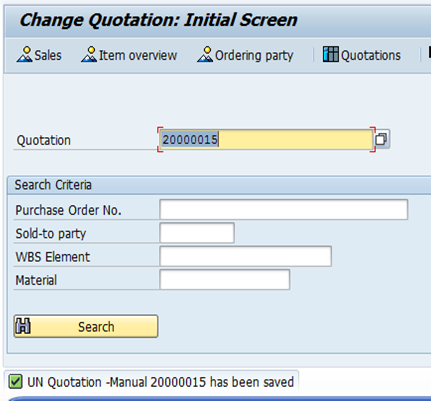
B.5.12. The quotation should print automatically. If not, press the Enter key on the keyboard to check for an error message.
Please refer also to steps 17 and 18 on pages 53 and 54 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for more printing information.
B.6. Create standard order / Transaction Code: VA01
B.6.1. The Sales Processor can create a standard order in the system independently or with reference to a quotation. Steps to create a standard order from a quotation are as follows:
B.6.1.1. Type VA01 in the Command field and click the Enter icon.
B.6.1.2. Click the Matchcode icon in the Order Type field.
Please refer to picture 'Create Sales Order: Initial Screen' of step 2 on page 65 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.6.1.3. Select the required order type from the displayed list.
B.6.1.4. Click the Continue icon.
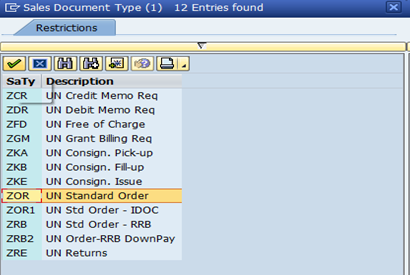
B.6.1.5. Click the Create with Reference button (applicable only to orders with reference to a Quotation).
Please refer to picture 'Create Sales Order: Initial Screen' of step 5 on page 67 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.6.1.6. Type the quotation number in the Quot. field in the Create with Reference pop-up window. Click the Copy button.
Note: If only certain line items of the Quotation will form part of the Standard Order, then click the Item Selection button instead of the Copy button. This will allow the user to choose only relevant line items for the new Standard Order to be created.
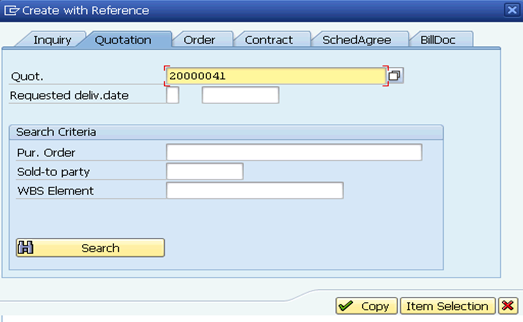
Please also refer to picture 'UN Quotation - Manual 20000015: Selection List for Reference Document' of step 7 on page 68 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.6.1.7. In the Header Section, type the PO number confirmed by the customer in the PO Number field.
Please also refer to picture 'Create UN Standard Order: Overview' of step 9 on page 69 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.6.1.8. In the Sales tab, the SD User can populate or verify information displayed in the Item, Material, Order Quantity, Amount, Currency and Plant fields. Change the Item Category, if required. Then change the line item status to RES - Approval Requested to submit the line item for approval by the SD Approver.
Please also refer to picture 'Create UN Standard Order: Overview' of step 11 on page 70 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
Please refer also to steps 10-24 on pages 69-75 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for more information on creating a standard order.
B.6.2. The steps to create a standard order without reference to a quote are very similar to the above mentioned process. The following steps vary from the process above:
B.6.2.1. Instead of clicking the create with reference button, populate the following fields and click the Enter icon:
• Order type
• Sales Organization
• Distribution Channel
• Division
• Sales Office
• Sales Group
B.6.2.2. In the Header section, type the PO number confirmed by the customer in the PO Number field. Also populate the Sold-to Party fields.
Please also refer to pages 76-82 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for detailed information on 'Display or Change a Sales Order - VA03 & VA02'.
B.7. Approve the Standard Order / Transaction Code: V.26/VA.02/VA.05
B.7.1. Type V.26 in the Command field and click the Enter icon and click the Variant icon.
B.7.2. Select the variant 'UN Orders Waiting Approval' and click the Continue icon.
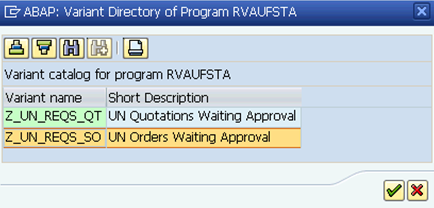
B.7.3. The required information is visible by default in the Sales Document Data section.
B.7.3.1. Enter the relevant Sales Area information to view orders assigned to the Approver
B.7.3.2. Click the Execute icon to obtain the list of orders pending approval.
B.7.4. Standard Orders, including Credit/Debit Memo Requests and Return Orders, with User Status = REQS-Approval Requested will be displayed.
B.7.5. Select the Standard Order to approve. Click the Enter icon or press the Enter key on the keyboard.

B.7.6. Review the document. When you are ready to approve, return to the Sales tab.
B.7.7. Change the line item status to APPR-Approved for the line item that needs to be approved.
· For line items that need to be rejected, change the line item status to REJT-Rejected.
B.7.8. Click the Save icon.
Please also refer to picture 'Change UN Standard Order 32: Overview' of step 20 on page 87 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
Please refer also to steps 21-23 on page 87 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for more information on approving a standard order.
B.8. System checks stock availability (ATP) / Automated
The system will automatically check stock availability, propose and confirm the quantity and delivery date.
B.9. Authorization of customer credit limit / Automated
B.9.1. The system will perform a credit limit check. Where a credit limit has been exceeded, approval will be required to release the order. The order must be 'unblocked' by the appropriate approver in order to enable creation of delivery documentation. Where a credit limit has been exceeded and approval is not granted to release the order, the customer is notified. The order will remain blocked in the system.
B.9.2. If the customer is paying with a credit card, the system will automatically obtain authorization and upon authorization approval, the authorization code will be captured in the order.
B.10. Create outbound delivery / Transaction Code: VL10H
B.10.1. The warehouse will process, pack and ship the delivery if the inventory and customer credit are confirmed. An integrated posting will be driven based on the movement of materials outline in the standard order.
Journal entries for the sale of a publication
The recognition of the cost of a publication sold would yield the following entries:
|
Date |
GL |
GL short description |
Debit |
Credit |
|
2 Feb 2014 |
77011010 |
Consu Publicati Sold |
100 |
|
|
|
17011010 |
Invn Publica forSale |
|
100 |
B.11. Create Invoice / Transaction Code: VF04
B.11.1. According to the order for inventory shipping completion status, the system will mark a document due for billing. For sales order for services the billing can be performed after sales order is approved. All billing relevant sales orders due for billing can be seen and maintained in Maintain Billing Due List screen by Finance (FA Senior User, Code: FA.05). The AR User will create an invoice from any standard order due for billing, review the accuracy of the invoice and issue it to the customer.
B.11.2. Once the invoice is paid, if the incoming payment contains information e.g. invoice number, that identifies an existing receivable for the same amount, Umoja will establish a match between the two. The receivable will be automatically cleared by the incoming payment. When there is no match (e.g. invoice number is the same but amounts differ), the automatic clearance will fail. A manual clearing will be performed in the AR unit.
NOTE: Refer to section 3.2.2 of Finance Manual Chapter on Accounts Receivable for details on incoming payment processing.
B.12. Posting of receivables / Automated
B.12.1. Revenues can be classified as i) internal (agencies included within Umoja scope) spendable; ii) internal non-spendable; iii) external (agencies outside of Umoja scope) spendable; and iv) external non-spendable. Spendable revenues are true cost recoveries, while non-spendable (i.e. real revenues) will be returned to Member States.
B.12.2. The system automatically assigns the appropriate document type to integrated transactions such as billing documents based on the transaction code used and posting rules configured. The document type determines which account types can be posted to. A separate number range is assigned to every document type. In Umoja, standard document types are used as well as a number of custom document types. More detail on document types (including a list of specific document types) can be found in section 3.1.1 of the Finance Manual Chapter on Accounts Receivable.
B.12.3. In SD, the account determination tables are maintained to derive the AR reconciliation account as well as the revenue GL account based on the chart of accounts, sales organization, distribution channel, division, item category, account assignment for customer, account assignment for material, and account key. Based on this information, the appropriate GL accounts are derived to post real time.
B.12.4. GL codes correspond to various classifications in the chart of accounts. Separate GL codes can exist for internal versus external and spendable versus non-spendable accounts. Below are classifications broken out by common indicators:
|
GL Account |
Description |
|
621XXXXX |
IS3 - Revenue producing activities for extension |
|
628XXXXX |
IS3 - Revenue producing activities for foundation |
|
6280XXXX |
UNPA |
|
6281XXXX |
Publications |
|
6282XXXX |
Services to visitors |
|
6283XXXX |
UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs |
|
6284XXXX |
Garage |
|
6285XXXX |
Gift items |
|
6286XXXX |
Newstands |
|
6287XXXX |
Catering |
|
6288XXXX |
Retail operated by contractor |
|
6289XXXX |
Rental retail space |
|
6290XXXX |
Rental Conference Center |
|
69XXXXXX |
IS 2 / misc - Other income, non-spendable |
|
691XXXXX |
IS 2, External |
|
692XXXXX |
IS 2, External |
|
693XXXXX |
IS2, internal |
|
694XXXXX |
Misc, internal |
|
631XXXXX |
Services rendered, spendable, external |
|
633XXXXX |
Services rendered, spendable, internal |
Journal entries for the sale of a publication
Recognition of revenue from a standard order sale of a publication to a commercial customer would yield the following entries:
|
Date |
GL |
GL short description |
Debit |
Credit |
|
2 Feb 2014 |
15101510 |
AR Exch Commercial Customer |
120 |
|
|
|
62811010 |
Sale IS3 Publication |
|
120 |
B.13. Delete standard order / Transaction Code: VA02
Please also refer to sections 'Delete the whole Sales Order - VA02' and 'Cancel or Reject Specific Line Item - VA02' on pages 78-82 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for more detailed information on deleting a standard order.
The below steps are to be followed when a standard sales order is required to be deleted. This is an optional step that does not need to be part of the sales lifecycle.
B.13.1. If not yet approved by the SD Approver, enter the T-code VA02 in the Command field.
B.13.1.1. Navigate to the standard order to be rejected.
B.13.1.2. Select the line item to be deleted and click the Delete Item icon.
B.13.2. If an invoice has already been approved by the SD Approver but not yet been issued, the SD User can delete the whole standard order or a line item. This action will automatically block a line or the entire standard order from being invoiced. To cancel a whole standard order:
B.13.2.1. Enter the T-code VA02 in the Command field.
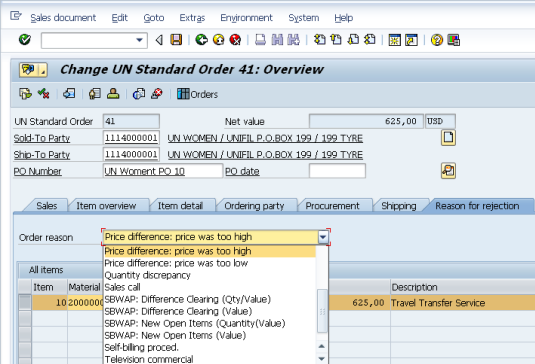
B.13.2.2. Navigate to the Standard Order you wish to reject.
B.13.2.3. Go into the Reason for Rejection tab.
B.13.2.4. Select an item from the Order Reason drop down menu.
B.13.2.5. Click Save.
B.13.3. To cancel an item from a standard order:
B.13.3.1. Enter the T-code VA02 in the Command field.
B.13.3.2. Navigate to a Standard Order you wish to reject.
Please also refer to picture 'Change UN Standard Order 212: Item Data' of step 1 on page 82 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
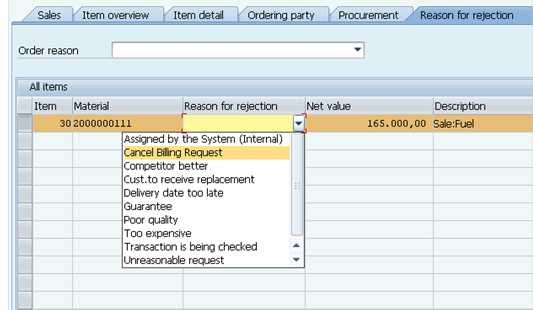
B.13.3.3. Go into the Reason for Rejection tab.
B.13.3.4. Select an item from the Reason for Rejection drop down menu.
Please also refer to picture of step 3 on page 82 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
B.13.3.5. Click Save.
Note: If an invoice has already been posted, the SD User will need to inform the Finance Account Senior User (by mail) and request to revert the posting.
3.2.2.2 Over the Counter Sales
The over the counter sales process is used in UN retail operations. The main focus in each store is the supply of master data from Umoja to the current Point of Sales (POS) systems (a system external to Umoja) and cash registers, as well as the receipt and posting of sales, goods movements and financial transactions sent from the current store systems to Umoja.
This integration process contains two major activities: Point of sales (POS) outbound and Point of Sales (POS) inbound.
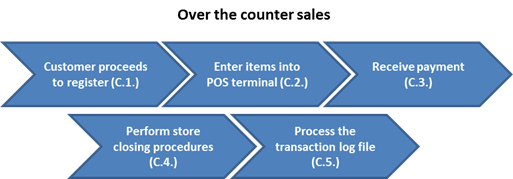
C. The over the counter sales process is as follows:
C.1. Customer proceeds to the register
C.1.1. The customer comes into the UNPA store or bookshop, selects an item and goes to the cashier. The cashier checks the stock availability in the system. POS Outbound activity supplies current master data from the backend system to the POS systems in the stores. Data is prepared individually for each store and relates only to its articles and prices.
C.1.2. Umoja will determine data changes by comparing the current date with the date of initialization. It will also determine changes within a specified lead time (i.e. transfer of POS master data that has changed since the last data was supplied). The changed data is then transferred to the POS systems.
C.1.3. If the stock is available, the cashier will settle the transaction with an accepted method of payment.
C.2. Enter item(s) into POS terminal
From the 'Enter item' prompt, the cashier will scan or enter the item into the POS terminal.
C.3. Receive payment
C.3.1. The cashier enters the payment method in the POS (cash or credit card). In UNPA, if credit card, the current system (QuickBooks) does not support a credit card process therefore an offline credit card authorization is required. In this case, cashiers use a separate credit card terminal to obtain the authorization. Once approved, this authorization number is manually entered into QuickBooks.
C.3.2. A receipt will be generated when the transaction is complete.
C.4. Preform store closing procedures
The cashier and store manager will perform store closing procedures by closing the POS terminal, consolidating store totals and printing store reports.
C.5. Process the transaction log file
The POS system will generate a transaction file with all the daily sales transactions for each store. The POS system will send the transaction log file to Umoja in the background processing through a nightly batch process.
C.5.1. POS Inbound is the nightly batch process that collects the data at the POS and transfers it to a central system for processing. The POS Inbound process is extremely critical in UN retail operations since the core functions of Umoja manage the distribution of goods to the customer. The stock levels are managed in Umoja and updated by goods movements and sales activities carried out at the POS. Based on this data, replenishment requirements are calculated on a central system. In order to avoid surplus or out of stock situations at the store, the passage of the sales information from the POS System to Umoja and potentially to a Forecast & Replenishment tool has to be secured and closely monitored.
C.5.2. In addition to updating stock levels, financial aspects also play an important role in the POS Inbound process. An invoice is created and will be posted according to the payment method used for sales. Cash payments are recognized as cash on hand. For credit card payments, the sales amount is posted in Accounts Receivable against the credit card provider and the payment will be settled later with reference to the approved authorization number.
3.2.2.3 Third Party Procurement
Third-party procurement occurs when a UN Agency or any other entity external to Umoja requests the UN to procure services or materials on its behalf. The UN may agree to purchase and pay for the goods or services on the condition that reimbursement is received before or after the goods/services are delivered. Once the order is placed, a quotation will be created, followed by a standard order. A requisition, purchase order and goods receipt will be created and an invoice receipt generated once the goods or services are received. Finally, an invoice will be sent to the third party.
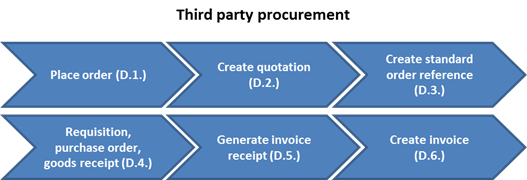
Please also refer to section 'Third-Party Procurement processing' on pages 101-103 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for more information.
D. The third party procurement process is as follows:
D.1. Place order
D.1.1. When the UN Agency or any other entity external to Umoja requests the UN to procure services or materials on its behalf, the UN may agree to purchase and pay for the goods or service and invoice the UN agency to recover the cost plus any other applicable fees
Example: UNIFIL purchases computers against an established UN System contract for UNCTAD.
D.2. Create quotation / Transaction Code: VA21
A quotation is created following the same steps as a standard order process.
Example: Procurement Officer at UNIFIL creates a quotation and sends it to UNCTAD for review and confirmation.
D.3. Create standard order reference / Transaction Code: VA01
A sales order is created following a similar process to standard orders. If the order is related to third party procurement, the user should change the item category to trigger the third party process. The sales order line items will automatically generate a purchase requisition.
D.3.1. Type VA01 in the Command field and click the Enter icon.
D.3.2. Type ZOR = UN Standard Order in the Order Type field.
D.3.3. Type the required data in the Sales Organization, Distribution Channel, Sales Office, Sales Group and Division fields. Click the Enter icon.
D.3.4. On the Create UN Standard Order: Overview screen, populate the following fields:
• Sold-To Party
• PO Number
• Material
• Order Quantity
• Amount
• Currency
• Plant
D.3.5. For all the line items, at the Item Detail level populate/review the following tabs:
· Sales A
· Sales B
· Shipping
· Billing Document
o Incoterms is required if purchasing goods
· Payment Terms
· Conditions
o Review whether standard Pricing Conditions have been applied correctly
o Type the additional Condition Type and Amount, as required
· Account Assignment
o Populate the Fund, Funds Center and Functional Area fields

D.3.6. Click the Matchcode icon in the Item Category field and select TAS - Third Party Item. Click the Enter icon.
D.3.7. If an advanced payment is required in association with third-party procurement, then the Item Category: ZTAS - Third Party Item w/DP should be used.
D.3.8. When the Enter Purchase Requisition screen appears, enter the Purchasing Group and Value Price. Save and note the Standard Order number.
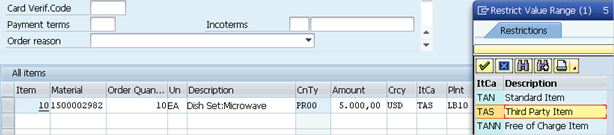
D.3.9. When the SD User enters the TAS condition, the Create Purchase Requisition screen appears.
D.3.10. Enter the Purchasing Group and Value Price. Click the Back icon.
D.3.11. Save and note the Standard Order number.
Example: Admin. Officer in UNIFIL Procurement creates a Standard Order for UNCTAD, which auto-generates a Purchase Requisition for approval by Chief Admin. Officer or Chief Procurement Officer.
D.4. Requisition, Purchase Order, Goods Receipt / SAP Portal
D.4.1. In the case of third party procurement, a requisition is created automatically, and then it is transferred to a PO once approved. The goods receipt will be statistically performed, and it will be referenced in the vendor invoice receipt. This step is part of the Umoja procurement process. For detail on the Umoja procurement processes, refer to Finance Manual Chapter Expenses (section 3.1).
Example: The Procurement Officer completes the solicitation exercise and uses the relevant purchase requisition to issue a Purchase Order to the successful vendor.
D.5. Generate invoice Receipt / Transaction Code: MIR7
Refer to Finance Manual Chapter on Accounts Payable - Invoice Processing with a PO (section 3.2.1), for the detailed process.
Example: UNIFIL receives and posts the invoice in the Umoja system. The system verifies that the items have been received, matches the received items against the PO and authorizes payment to the vendor.
D.6. Create Invoice / Transaction Code: VF04
According to the order shipping completion status or third party procurement completion update, the Billing Processor will create an invoice to bill the customer. Refer to Finance Manual Chapter on Accounts Receivable for details on customer invoice (section 3.2.1) and incoming payment processing (section 3.2.2).
In this situation, the UN is acting as an intermediary and thus is an agent (reference Revenue from Non-Exchange Transactions - Funding Agreements for detail on the distinction between agents versus principal).
Revenue and expenses will not be recorded where the UN is acting as an agent. Only the commission, if any, will be recorded as exchange revenue.
As per the example above, if the computer costs USD 500 and UNIFIL charges UNCTAD 5% for commission, only the 5% is recorded as revenue from an internal (two agencies within Umoja scope) transaction.
|
Date |
GL |
GL short description |
Debit |
Credit |
|
2 Feb 2014 |
19401010 |
AR DueTo From |
525 |
|
|
|
635XXXXX |
Commission account |
|
25 |
|
|
35101510 |
AP Commer Vendor |
|
500 |
As per the DFS directive issues in March 1999, an administrative charge of 14% should be added to all charges billed to 'non-secretariat entities' as 'miscellaneous income'.
Charges for repair and maintenance services for UN specialized agencies and non-secretariat entities should be charged as follows:
a. Labor (int. and nat. staff) - USD 15 / hr.
b. Parts - actual costs (cost recovery)
c. Petrol - actual costs (cost recovery)
d. administrative fees - 14% of total cost
3.2.2.4 Customer Consignment
Once an agent/distributor orders products (through fill-up orders), the orders are processed and delivered to the agent/distributor's stores. The agent/distributor will periodically report items that have been sold to the end customer, at which point the UN will bill the agent/distributor. At the end of the relationship, a pick-up order may be used to return any unsold consigned products to the UN. In UN operations, orders are received by mail, telephone, or fax. The consignment process pertains to the sale of stamps and publications.
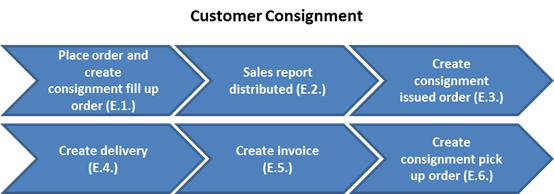
Please also refer to section 'Sales Consignment Order' on pages 96-98 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for more information.
E. The customer consignment process is as follows:
E.1. Place order and create consignment fill-up order / Transaction Code: VA01
E.1.1. The distributor/agent will place an order and the Sales Processor will create a consignment fill-up order in the system. During the order process, the system will automatically check the available stock and provide a warning if there is not sufficient stock to promise the customer. Available to promise (ATP) stock is calculated as; warehouse stock + planned receipts - planned issues.
E.1.2. A customer master data record will be created for new distributors/agents. A customer can be an individual or an organization.
E.1.3. If stock is available, the warehouse will process the delivery, pick, pack and ship the order.
E.2. Sales report is distributed periodically / Manual
The agent/distributor will periodically distribute a sales report to the UN, identifying which items have been sold. The agent/distributor manages the stock of products at their store (s). The UN retains ownership of the products until they are sold to the end customer.
E.3. Create consignment issue order / Transaction Code: VA01
Once the Sales Processor receives the sales report they will create a consignment issue order in Umoja identifying the items sold.
E.4. Create delivery / Transaction Code: VL10H
The Shipping Processor will create delivery for the items sold based on the consignment issue order and post the goods issued in the system. Since the stock was already in the distributors' warehouse, no actual product needs to be shipped; only the stock status is updated.
E.5. Create invoice / Transaction Code: VF04
E.5.1. The Billing Processor will create an invoice to bill the distributor for the product which has been sold to the end customer based on the consignment issue order.
E.5.2. When a billing document is created, the billing data is forwarded to Financial Accounting. Revenue is recognized by the UN when the goods are sold by the distributor/agent to a third party. The accounting entries and appropriate GL accounts are identified in the back ground processing based on tables within Umoja. The financial accounting data will be posted in real-time.
E.6. Create consignment pick-up order / Transaction Code: VA01
E.6.1. According to the agreement, the unsold items may be returned to the UN periodically. The Sales Processor will create a consignment pick-up order in Umoja.
E.6.2. The Sales Processor notifies the agent/distributor with the pick-up order number so that the product can be shipped back with reference to the order. No credit or debit invoice will need to be created.
3.2.2.5 Standing Order
The standing order process which is catered for UN Postal stamps is not in scope for Umoja Foundation but will be covered in Extension 1. In summary, stamp collectors of the UN require automatic fulfillment of their order whenever a new stamp edition is released.
The journal entries for a standing order would be as follows:
Journal Entries (sale to commercial customers) (automated process during goods issue for outbound deliveries)
Recognition of cost of goods sold:
|
Date |
GL |
GL short description |
Debit |
Credit |
|
2 Feb 2014 |
77011010 |
Consu Publicati Sold |
100 |
|
|
|
17011010 |
Invn Publica forSale |
|
100 |
Recognition of revenue (automated process during creation of invoices):
|
Date |
GL |
GL short description |
Debit |
Credit |
|
2 Feb 2014 |
15101510 |
AR Exch Commercial Customer |
120 |
|
|
|
62812010 |
Sale IS3 PublicSubsc |
|
120 |
3.2.3 Post Sale Processes
Post sale processes include return of goods and credit/debit memos.
3.2.3.1 Return of Goods
Sales Order Processing - Return Order includes receiving customer requests for return of products, processing return deliveries and generating a credit note. In UN operations, return orders are received by mail, telephone, or fax. A centralized order management system will provide visibility of the order status, stock level and financial accounting data.
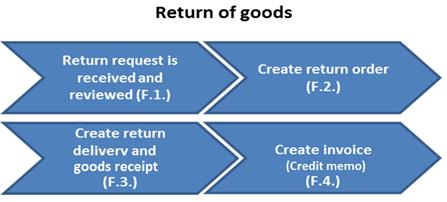
F. The return order process is as follows:
F.1. Customer requests return and return request is reviewed / Manual
Customer requests a return via mail, telephone or fax due to the wrong shipment or product damage during shipping. A return order can be referenced to the original sales order or it could be created as a stand-alone return order. Return Approver will review and approve or reject the order. If the return request is rejected, the customer will be notified with a rejection reason.
F.2. Create return order / Transaction Code: VA01
If the return order is approved, the Sales Processor will create a return order in the system. The customer can then ship the return product(s) with the return order number.
F.3. Create return delivery and goods receipt / Transaction Code: VL10H
F.3.1. The shipping processor will create a return delivery order upon arrival of the returned product. They will enter values:
• Shipping point/Receiving point
• Document Type
• Sales Document No
F.3.2. They will check header, item data and the document flow.
F.3.3. The document will be saved and the stock will be posted into return stock for inspection, when the goods receipt is performed.
F.4. Create invoice (credit memo) / Transaction Code: VF04
F.4.1. Once the inventory is received and quality is inspected by the UN, an invoice will be generated with reference to the return order to refund the customer. If the product is sold in a different currency from the face value, it is important to use the exchange rate at the time of the original sale. The system will automatically propose the original exchange rate in the return order based on the pricing date.
F.4.2. When a billing document is created, the billing data is forwarded to Financial Accounting. The accounting entries and appropriate GL accounts are identified in the back ground processing based on tables within Umoja. The financial accounting data will be posted in real-time.
Please also refer to pages 104-105 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for information on process deviation from standard order.
Journal Entries (sale to commercial customers)
If goods are returned within the same accounting period in which they were purchased, an offsetting entry will be created to reverse the revenue. If the goods are returned in the accounting period subsequent to the accounting period in which they were purchased, the return entry will be made in the period in which the goods were returned (and not the period in which they were purchased).
The recognition of a returned publication would yield the following entries:
|
Date |
GL |
GL short description |
Debit |
Credit |
|
2 Feb 2014 |
17011010 |
Invn Publica forSale |
100 |
|
|
|
77011010 |
Consu Publicati Sold |
|
100 |
The recognition of the reversal of revenue from a returned publication would yield the following entries:
|
Date |
GL |
GL short description |
Debit |
Credit |
|
2 Feb 2014 |
62811010 |
Sale IS3 Publication |
120 |
|
|
|
15101510 |
AR Exch Commercial Customer |
|
120 |
3.2.3.2 Credit and Debit Memos
The credit/debit request is used to correct any over/under charges to/from the customer. It is created with reference to the original invoice. An order reason code will be assigned to each order. Once complete, a debit or credit memo is generated.
Please also refer to section 'Credit/Debit Memo Request' on page 105 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for more information.

G. The credit and debit memo process is as follows:
G.1. Customer requests a credit/debit / Manual process through email or phone.
A customer can request a refund which will be created with reference to the original invoice.
G.2. Create credit/debit memo request / Transaction Code: VA01
G.2.1. Type the T-code VA01 in the Command field and press Enter.
G.2.2. Type ZCR - Credit Memo Req or ZDR - Debit Memo Req in the Order Type field.
G.2.3. Click the Create with Reference button to create a Credit/Debit Memo Request against an invoice or order that has been issued.
Please also refer to picture 'Create Sales Order: Initial Screen' on page 105 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
Otherwise, type 1000 in the Sales Organization field, appropriate Distribution Channel, Division, Sales Office and Sales Group then click the Enter icon to create a Credit/Debit memo request without any reference to an invoice or order.
G.2.4. In the BillDoc tab, type the reference Invoice number in the Billing Document field.
G.2.5. Alternatively, in the Order tab, type the reference order number in the Order field.
Please also refer to the first picture on page 106 of UMOJA Sales and Distribution User Guide for illustration.
G.2.6. Click the Item Selection button.
G.2.7. Choose the material for which the Credit/Debit transaction needs to be applied on.
G.2.8. Click the Copy button.

G.2.9. In the Create/Debit Memo Req Overview screen, at the header level, type the Customer Reference PO number in the PO Number field.
G.2.10. Depending on the type of credit/debit transaction, the user may:
G.2.10.1. In Sales A tab, change the quantity in the Target quantity field.
G.2.10.2. In the Conditions tab, change charges/price.
G.2.10.3. In the Sales tab, change the status to REQS-Approval Requested for the required line item. Click the Back button and Save.
G.2.10.4. Note the newly created credit/debit memo request number.
G.3. Create credit/debit memo / Transaction Code: VF04
If the credit/debit request has been approved and the billing block is removed, a credit/debit memo will be created to debit/credit the customer account.
When a billing document is created, the billing data is forwarded to Financial Accounting. The accounting entries and appropriate GL accounts are identified in the back ground processing based on tables within Umoja. The financial accounting data will be posted in real-time.
Journal Entries (credit for commercial customer)
The following entries would be applicable to a credit for a guided visitor tour:
|
Date |
GL |
GL short description |
Debit |
Credit |
|
2 Feb 2014 |
62821010 |
Sale IS3 VisitGuidTr |
100 |
|
|
|
15101510 |
AR Ex Customer |
|
100 |
3.2.4 Special Cases
Garage and accommodation processing do not follow the typical sales processes described in the sales process section above, and thus are included in the special cases section. The section starts with garage operations, for which there are two different processes - long term pass operations and short term pass operations.
3.2.4.1 Garage Operations
The Garage Administration Process involves creating and managing short and long term parking permits for both employees and external customers.
3.2.4.1.1 Long Term Pass Garage Operations
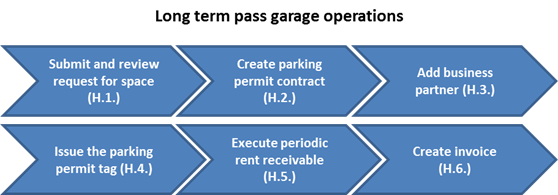
H. The long term pass garage administration process is as follows:
H.1. Submit and review request for space / Manual
A request for a parking space is created by the organizational entity. The request reviewer will review the request and run a report showing parking space availability. If spaces are available, a parking permit will be created.
H.2. Create parking permit contract
A parking permit for decals and medallions will be created. Permit details such as contract term dates, renewal option, notice option, frequency of payment, conditions (parking fees) and parking space will be entered.
H.3. Add business partner / Transaction Code: BP
An Internal Business Partner (employee) or external business partner (customer) will be assigned to the contract permit.
H.4. Issue the parking permit tag (i.e. decal/medallion)
H.5. Execute periodic rent receivables
The accounting flows resulting from the conditions are posted while taking into account the contract type.
Journal Entries (sale to commercial customer)
Recognition of revenue from a sale of a monthly parking pass to a commercial customer would yield the following entries:
|
Date |
GL |
GL short description |
Debit |
Credit |
|
2 Feb 2014 |
15101510 |
AR Exch Commercial Customer |
150 |
|
|
|
62841010 |
Sale IS3 GarMonthFee |
|
150 |
H.6. Create invoice / Transaction Code: VF04
Create and print parking fee (rent) invoices based on financial documents that are generated from periodic postings. These documents will be printed and mailed to customer.
3.2.4.1.2 Daily Pass Garage Operations

I. The short term pass garage administration process is as follows:
I.1. Submit and review request for space
A request for a parking space is created by the organizational entity. The request reviewer will review the request and download and edit the daily parking request list.
I.2. Download, edit and send list to security
The supervisor will download and edit the daily parking request list. The list will be provided to security.
I.3. Record the payment
Cash will be collected, payment details will be entered into the system and a receivable will be created.
Journal Entries (sale to commercial customer)
Recognition of revenue from a sale of a daily parking pass to a commercial customer would yield the following entries:
|
Date |
GL |
GL short description |
Debit |
Credit |
|
2 Feb 2014 |
15101510 |
AR Exch Commercial Customer |
20 |
|
|
|
62842010 |
Sale IS3 Gara Ticket |
|
20 |
3.2.4.2 Accommodations and Lodging
Accommodations in Peacekeeping Missions are the service provided to staff members for internal travel and on an exceptional basis to an external customer. The rooms will be established as master data in the system. When a staff member or customer requests to reserve a room and the accommodation processor can check the room availability, the room will be booked in the system accordingly. An invoice will be generated to bill the staff member or customer according to the reservation. The charges can be billed to a staff member or deducted by payroll.
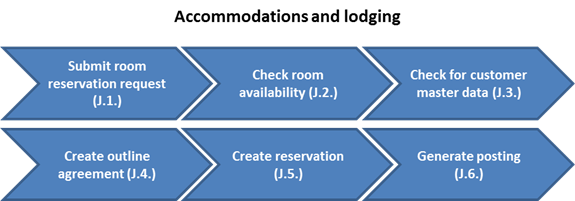
J. The accommodation and lodging sales order process is as follows:
J.1. Submit room reservation request
The customer can submit a request through the E-commerce online shop. For staff members, the online shop can be accessed through the portal.
J.2. Check room availability
Upon receipt of a customer request for reservation, the accommodation processor can check if the requested room is available through the system. If the room is not available, the accommodation processor will inform the customer.
J.3. Check for customer master data / Transaction Code: BP
The accommodation processor will check if the customer master data already exists in the system. If the customer data does not exist in the system, a business partner will need to be created.
J.4. Create outline agreement
If the occupant requires the room for a long term and requires periodical billing, then an outline agreement should be created by the accommodation processor. This is only necessary if the customer requires the room for a long period of time.
J.5. Create reservation
The accommodation processor will create the individual reservation and assign the outline agreement for a long term occupancy. For a short-term occupancy, the administrator will directly create an individual reservation.
J.6. Posting / Automated
For a long term occupancy customer, the billing processor will post periodical billing against the outline agreement. If a short-term occupancy and only one-time billing is required, then the billing processor will post onetime billing to the reservation.
If the UN provides accommodations to UN agencies external to Umoja, the following GL entries will be used:
|
Date |
GL |
GL short description |
Debit |
Credit |
|
2 Feb 2014 |
15101310 |
AR Ex UN Family |
150 |
|
|
|
628XXXXX |
Sale IS3Accommodations and lodging |
|
150 |
3.2.4.3 Closing Entries for Income
Accounts Division forwards a fax every other year after the closing of the biennium. Missions are required to ensure closing entries are recorded in UMOJA when received for 'income'.
3.2.4.4 Stale and Outstanding Cheques
After a six-month period of cheques not cashed, Finance should transfer the cheque amount by way of a debit to stale/outdated and credit to 'miscellaneous income' account.
3.2.4.5 Gains on Currency Exchange
Missions should reflect income generated due to gains on exchange on a monthly basis.
3.2.4.6 Accounting For Cases with Property Survey Board
LSPB requires that in cases where HSPB determines an assessment is to be reduced, the reduced portion is to be reflected in the 'miscellaneous income' account.
4 Business Partners
The use of SAP Business Partner functionality is core to the Umoja solution when processing transactions. Each module enables specific processes and requires the creation of a customer, vendor and/or BP. For commercial operations, a BP with the role of UN Customer will need to be established. The following Business Partners are relevant to this chapter:
· Z011 Member States
· Z012 Non Member States
· Z014 UN Agency Funds and Programmes
· Z013 Government
· Z015 Non-Governmental Organizations & Intergovernmental
· Z016 Individual External, Non-Staff (this group is not on Payroll)
· Z018 Commercial Customers
· Z020 Staff Members, Ex-Staff Members, Survivors, Dependents
· Z021 Non Staff Military/Police
December, 2016