1 Objective
The objective of this chapter is to give a brief overview of the Umoja enterprise structure and the relevant master data elements used in the coding block structure within the Umoja environment. It aims to provide high-level understanding of the assignment of master data elements and how it impacts the derivation of linked master data elements to ensure the business transaction is captured accurately in accordance with the UN's classification and reporting requirements.
2 Umoja Enterprise Structure
2.1 Introduction to Umoja Enterprise Structure
The Umoja enterprise structure is simply the organizational structure that represents the UN Secretariat in SAP environment. In the UN, the foundational enterprise structure starts with the Company Code, Controlling (CO) area, and Fund Management (FM) area. Grants Management, from an enterprise structure perspective falls under FM area.
The Umoja enterprise structure design is a fundamental step in the UN transformation initiative. Its design is driven by how business scenarios are processed, how balances are aggregated, and how reports are generated for an enterprise. Additionally, the enterprise structure design is flexible enough to integrate the different enterprise structure elements into the overall structure of UN organization and scalable enough to accommodate the UN's current and future business requirements.
Below the foundational elements, it consists of specific elements from various modules which for legal reasons or other specific business related purposes are grouped together for example Supply Chain Management (SCM) or Human Capital Management (HCM). Together with the Foundations Elements, the composition of these Enterprise Structure Elements is illustrated below.
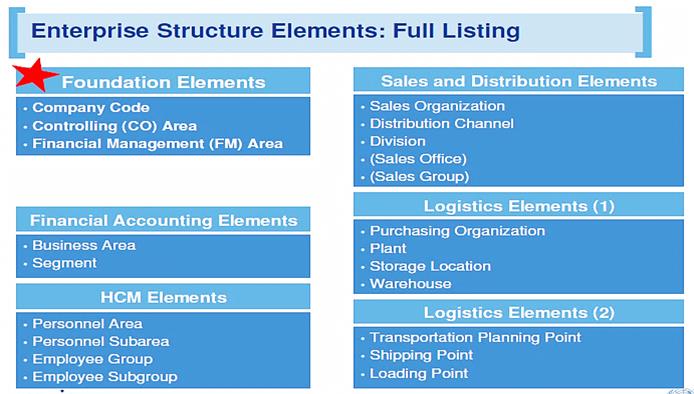
2.1.1 Umoja Enterprise Structure Terminology
2.1.1.1 Foundation Elements
• The Company Code is the highest enterprise structure element in the hierarchy where complete financial statements can be generated. In SAP, it is typically synonymous to the legal entity or external view of an organization. All structures within a Company Code have similar financial processes and use the same chart of accounts. Similarly, every financial transaction relevant to the external view is assigned to a Company Code. In Umoja, only Company Code 1000 is set up for both Peacekeeping missions (PK) and Non-Peacekeeping Operations.
• The CO (Controlling) area defines the context where cost (management) accounting takes place; it's about revenue and costs, including appropriate internal allocation and distribution. All revenue and cost transactions which are posted in Financial Accounting (FI) are also posted in CO area. The CO area must be assigned to Company Code to ensure transactions from FI are forwarded to CO area.
• The FM Area represents the organizational unit which plans, controls and monitors funds and the associated budgets to ensure budgetary control is established for the organization. Once the FM is activated in the Company Code 1000, posting transactions from upstream modules like FI and SCM are recorded as commitment and actual data in FM.
2.1.1.2 Financial Accounting Elements
• Business Area is an enterprise structure element from FI that represents a separate area of operations for Peacekeeping (PK) and Non-Peacekeeping (NPK) entities in UN. From a business area perspective, internal financial statements can be generated per entity to provide UN a tool to analyze each PK and NPK entity's area of responsibility.
• Segment is another enterprise structure element from FI that represents a 'budget pillar' based on the current structure used for 'volumes' of Financial Statements as required by IPSAS. In Umoja, the value of segment is derived from the functional area.
2.1.1.3 Supply Chain Management (SCM) Elements
• Purchasing Organization is an organizational level that negotiates conditions of purchase with vendors for one or more plants or companies. It assumes legal responsibility for all external purchase transactions.
• Plant is an organizational unit which serves to subdivide an organization according to production, procurement, maintenance, materials planning and materials valuation.
• Storage Location represents a physical segregation of inventory or materials.
• Warehouse is a systematic representation of the physical layout of a storage facility, a logical grouping of storage locations.
• Transportation Planning Point is for planning shipments with particular features. A shipment is assigned to one transportation planning point e.g. by train, by ship, or by air.
• Shipping Point is the physical location to which the inventory or materials are shipped.
• Loading Point is the subdivision of Shipping Point.
2.1.1.4 Human Capital Management (HCM) Elements
• Personnel Area is a unit in personnel administration, which represents a Country in Umoja.
• Personnel Subarea is subdivisions of the Personnel Area, which represents a Duty Station in Umoja.
• Employee Group represents a defined grouping of work rules, for example, authorization checks, remuneration levels, or work schedules. In Umoja, the employee type relates to employee group which can be International Staff or Local Staff.
• Employee Subgroup is a subdivision of the Employee Group where for example, International Staff can be further be grouped into Professional or Field Service.
2.1.1.5 Sales and Distribution (SD) Elements
• Sales Organization is the organizational unit responsible for distributing goods and services, negotiating conditions of sale and other sales related activities.
• Distribution Channel is a means through which saleable materials or services reach the customer; the method of distribution.
• Division is a means of grouping materials or services, not just for sales and distribution purposes, but also for materials management i.e. product lines.
• Sales Office is a location for sales and distribution activities.
• Sales Group is assigned to Sales Office to differentiate different products or services being offered in Sales Office. It also creates different areas of responsibility within the Sales Office.
2.1.2 Subset of 'Full' Umoja Enterprise Structure
The subset represents a current snap shot of what comprises the Umoja Enterprise Structure. In the future, as more entities are added it will grow bigger with additional plants, distribution channels, and personnel areas.
Below is a graphical representation of subset of 'full' Umoja Enterprise Structure:

3 Master Data
3.1 Introduction to Master Data
Every organization like UN runs on data and a set of processes. As the level of information increases over time, data becomes complex and difficult to manage. If data is not stored and maintained properly, it leads to significant losses in productivity across the organization. Thus, it is extremely critical for the organization to create a centralized data source. In Umoja, this centralized data is called Master Data.
The Umoja system structures data into different groups, depending on its function and purpose.
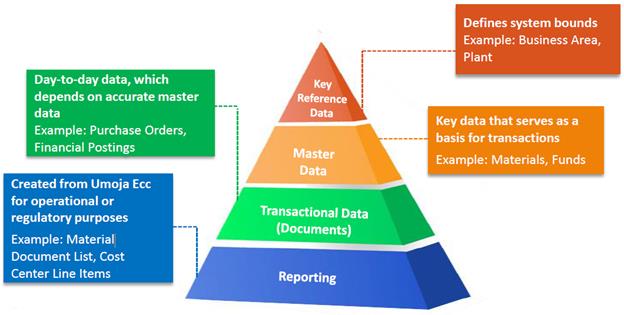
3.1.1 Umoja Terminology
Key Reference Data is set up to configure the Umoja system for specific needs of the UN. It defines the highest level boundaries in the Umoja system. It tends to be static and generally does not change after it has been added to the system. One example of key reference data is Business Area.
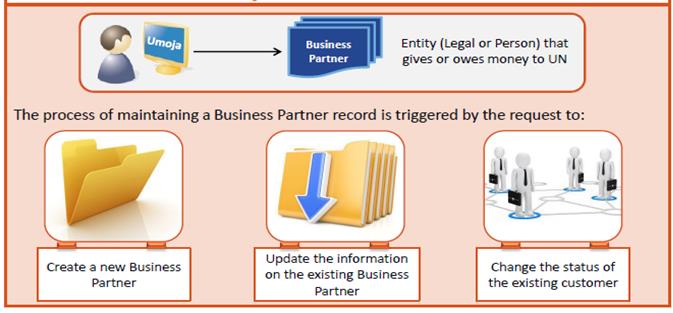
Master Data is centralized data used to support business processes across the organization. It drives all business transactions, applications, reports and decisions and creates a single source of records and reports for an organization. It is shared or linked across modules avoiding the need to enter data in various application areas. One example of master data which is used across different modules is business partners (BP).
Transactional Data is output data derived from processing business transactions in Umoja. The accumulated transactional data are stored in Umoja with drill down functionality from one transactional data in one module to go to another transactional data in another module. For example, a material document created from goods receipt can be displayed in Procurement but user can also display the related accounting document created in Financial Accounting module.
Reporting is the grouping of transactional data across different areas and different parameters. Standard reports as well as custom reports are available in Umoja environment.
3.1.2 Umoja Coding Block Elements
In Umoja, a large set of master data has to be maintained to process the business transactions from one functional module to the next. To illustrate, a Business Partner (BP) with a Vendor Role will only be entered once during the creation of purchase requisition (PR) or purchase order (PO), the same BP will be retrieved based on PO during good receipts or service receipts, and as well as during logistics invoice processing (LIV) when the vendor's billing invoice is received.
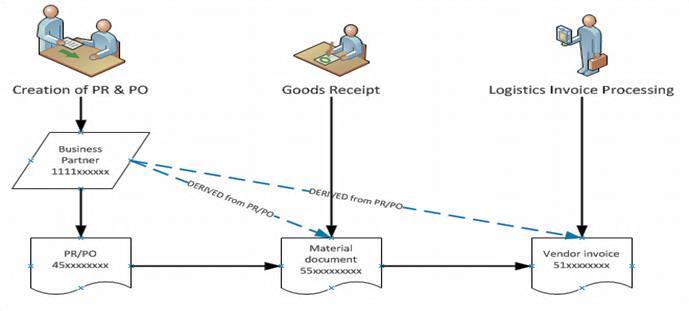
Similarly, to enable 'simultaneous posting' when a business user is posting a business transaction in Financial Accounting, the master data elements in each of the following modules must be linked together:
· Financial Accounting (FI)
· Controlling (CO)
· Funds Management (FM)
· Grants Management (GM)
The Master Data from each module, in addition to some Key Reference Data, make up the Umoja Coding Block elements.
The corresponding coding block elements for each module and ledger are as follows:

3.1.2.1 Financial Accounting (FI)
General Ledger (GL) accounts are maintained in Umoja Chart of Accounts '1000' and have 8 characters using transaction code FS00. Transaction code FS00 is used to maintain individual GL accounts in chart of accounts 1000. GL accounts receive the debit and credit value postings for various transactions and rolls ups to support the account balances in the financial statements.
The chart of accounts on the General Ledger are as follows:

Fiscal Year is a key reference data which is usually a period of twelve months or more for which an Organization like UN issues Financial Statements. A fiscal year may correspond to a calendar year but it is not obligatory. In Umoja, Fiscal Year Variant K4 is assigned to Company Code '1000' which means the Fiscal Year is divided into 12 posting periods plus 4 special periods.
Special periods are additional periods that can be used to record year-end adjustments such as late adjustments, audit adjustments, etc. Although the UN anticipates not being able to use the special periods as a result of the decision to keep the current Leading and Non-Leading ledger completely in sync, four special periods, the maximum number, were included in the configuration of the Leading ledger to allow for an eventual usage if SAP provides a fix in a subsequent update.
Interaction of Company Code and Fiscal year:
· All UN programmes and funds within the Umoja solution are defined within a single Company and Company Code 1000; this includes all Peacekeeping funds and all Non-Peacekeeping funds.
· The Company Code is defined with a fiscal year variant of K4 starting 1st January to 31st December, mapped to a calendar year. Therefore, the Leading Ledger view '0L' of transactions for the Company Code 1000 will be on a 1st January to 31st December basis.
· For Non-Peacekeeping funds the fiscal year is the calendar year; the same as the Company Code 1000. Therefore the Leading Ledger will be the source for Non-Peacekeeping reporting.
· For Peacekeeping funds the fiscal year 'Z6' is 1st July to 30th June. To support the Peacekeeping reporting a Non-Leading Ledger 'NL' will be defined for the UN Company Code, with a fiscal year of 1st July to 30th June assigned.
· For calculation of average daily balance (ADB) used in allocation of investment income, the fiscal year 'AD' is created based on 366 calendar days or posting periods. To support the investment accounting, a Non-Leading Ledger 'AD' is defined for the Company Code 1000.
· The Non-Leading Ledgers receives all financial postings that are made to the Leading Ledger and it will be the source for Peacekeeping funds reporting and ADB calculations in investment accounting.
For definition of Business Area and Segment, refer to section 2.1.1.2 Financial Accounting Elements.
3.1.2.2 Controlling (CO)
Cost Element is a cost or revenue item that is linked one-for-one to an expense or revenue GL account. The primary cost element is automatically created when the corresponding cost and revenue GL account is also created.
Cost Center is cost object that collects costs and revenues which identifies the areas of ongoing cost responsibility within an organization's overall organizational structure. In Umoja, every cost center links to a funds center. Cost center is created using transaction code KS01.
Internal Order is another cost object that collects costs and revenues of a specific event or simple project that has defined start and end dates, is usually temporary (unique) in nature and where costs should be segregated from other events or on-going operations to enable more detailed monitoring. Internal order is created using transaction code KO01.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Element is structural element in a project which divides the project into manageable units, defines specific dates, and collects costs. WBS Element is created using transaction code CJ91.
Profit Centers is an attribute of cost objects (Cost Center, Internal Order and WBSE) that allows reporting of costs by business function (e.g. finance, HR, IT, etc.). In revenue-producing areas, it supports reporting on products and services. Profit center is created using transaction code KE51.
3.1.2.3 Funds Management (FM)
Commitment Item is a functional grouping of costs and revenues. Commitment items classify budget transactions and business transactions affecting liquidity into revenue, expenditure, and cash balance items. In Umoja, typically there is one to one relationship between expense and revenue GL accounts in FI, cost elements in CO, and commitment items in FM. During transaction entry, the commitment item can be derived from GL account and/or cost element. Commitment item master record is created using transaction code FMCIA.
Fund is the lowest level source of funding used for tracking, controlling and reporting on available financial resources. In Umoja, fund is one of the document split characteristics to enable all accounting documents posted to split balanced postings per business area, segment, fund, and grant to report on financial statements per fund. Fund master record is created using transaction code FM51.
Fund Center is an organizational unit within FM assigned with area of responsibility such a department or a section unit within a department or project. A Fund Center controls budget and is time dependent. In Umoja, there is a one to one relationship between a fund center to a cost center. Fund Center is created using transaction code FMSA.
Funded Program as defined in Umoja is the program operational purpose and with definite timeframe. It can range from simple activities to complex projects and can cross fiscal years, funding sources and organizational units. Every internal order and every project WBSE will be assigned to a Funded Program in FM as required for budget control using an attribute on the internal order and WBSE 'Budget Control IO/WBSE'. Funded Program can be created using transaction code FMMEASURE.
Functional Area is used to classify revenues and expenditures of an organization by function. It provides a programmatic view of the UN from a budgetary perspective. Functional area is created using transaction code FM_FUNCTION.
Budget Period is the period of available budget authority. It enables to record budget appropriation/execution items independently of the fiscal year or any other master data information. In Umoja, Budget Periods will be used to enable biennial budget periods for Regular Budget (RB), annual budgets for Peacekeeping (PK) and annual budgets for trust funds and voluntary contributions. The Fund Type in combination with the posting date will be used to derive the Budget Period. Budget Period is created using transaction code FMBPD.
3.1.2.4 Grants Management (GM)
Sponsored Classes are used to provide budgetary control and to support reporting to Donors based on their specific requirements. Sponsored classes summarize the sponsor's expense and revenue categories and represent an alternative view of Umoja's Chart of Accounts. Each Sponsored Class represents a group of GL accounts. Sponsored Class can be created using transaction code GMCLASS.
Grant is used to maintain the terms and conditions of the Grantor's contribution through its lifecycle from proposal to execution to final close of the grant. In cases where the UN is a Grantee, that is the UN receives contributions from Donors, the Grant represents the Donor's Agreement. In cases where the UN is a Grantor, that is the UN gives money to an Implementing Partner, the Grant represents the Funding Agreement. Grant master record can be created using transaction code GMGRANT.
Sponsored Program represents the view the sponsor wants the data reported back to them and to enforce sponsor restrictions and requirements which cross grants. In Umoja, if a contribution is earmarked for a specific activity and donor requires reports to link the contribution to activities, this contribution will be represented by a single sponsored program. Contributions of donors without requirement for exact reporting or earmarking will be grouped in sponsored programs with like earmarks. Sponsored Program can be created using transaction code GMPROGRAM.
Grant Validity Period is assigned in Grant master record which determines the start and end date of Grant.
3.2 Business Partners
The SAP Business Partner functionality allows the creation and management of business partners centrally. The SAP Business Partner data object is designed to provide technical benefits such as data integrity and freedom from data redundancy. The data that is common to multiple roles does not have to be created each time, meaning that redundant data creation and retention is avoided, and that data inconsistencies are avoided.
A Business Partner (BP) is an important Master Data type. It defines the person, group or an organization with whom UN has a business interest.
Key components of the general BP Master Data include:

To achieve one Master Data record per entity, each Business Partner is defined through two dimensions in Umoja: Groups and Roles. Each Business Partner belongs to one group, but can be assigned one or more different roles. The roles ultimately determine how a Business Partner can be used in Umoja.
3.2.1 Business Partner Groups
|
Business Partner Grouping |
Organizations/Description |
|
Third party: |
|
|
Member States (Permanent Mission) |
|
|
Non-Member State (Holy See etc.) |
· Vatican · Palestine |
|
Government and Local Authority |
· Ministries (e.g. Ministry of Finance, SPAIN) · Governmental agencies (CIDA) · Municipalities (e.g. City of New York) |
|
UN Agency, Fund and Programme |
|
|
Inter Governmental and NGO |
· All non-UN and international organizations · All Non-governmental organization (NGO) (legally constituted organization created by natural or legal persons that operates independently from any form of government.) · Clubs · Schools · University Clubs · Associations |
|
Commercial: |
|
|
Commercial Vendor (UNGM) |
UNGM is the procurement portal of the UN System. It acts as a single window, through which potential suppliers may register with the 20 UN Agencies using the UNGM as their supplier roster. Vendors registered in UNGM are commercial entities which sell goods or services to the UN. Vendors that do regular business with the UN, or one-time vendors who are providing goods/services valued at over USD 4,000 must register in UNGM before a Contract or PO can be signed. The UNGM and Umoja integration allows for information from UNGM to be populated in ECC as a Business Partner. Commercial companies cannot be created in the Umoja system directly as BP with UN Vendor Role. |
|
Commercial Customer |
Companies that made payments to the UN has to be created as BP with 'UN Customer' role in Umoja. Commercial customers may be UNGM registered vendors, in which case two BP numbers have to be created and linked due to UNGM integration requirement. This does not apply to non-commercial entities (i.e. one BP number with both UN Vendor and UN Customer roles). |
|
Vendor (Non-UNGM) |
Vendors used for Low Value Acquisitions (purchases totaled below USD 4,000) do not have to register in UNGM even though UNGM registration is encouraged. They can be created directly in the Umoja system as BP with 'UN Low-value Vendor' role. |
|
Individuals: |
|
|
Individuals externals, Non-staff |
· Legal Committee Members, Judges · Meeting Participants, Travellers · Candidates/Applicants · Eminent Persons (VIPs) · Diplomats · Staff of UN agencies · Consultants, Individual Contractors · TC Experts on NR Loan - experts on loan to the UN from Governments Intern · Scholars, Fellows · Gratis Personnel - Type 2 · UN Volunteers (UNV) · Postal Workers |
|
Staff Member, Ex-Staff Member, Retirees, Survivors |
· UN Staff Members · Ex-Staff Members · Survivors and Dependents · Retirees |
|
Non-Staff Military and Police |
|
|
Treasury: |
|
|
Treasury Partner |
The Treasury Business Partners are the persons or legal entities with whom the UN Treasury enters into purchase/sale transactions of investment or FX instruments, and keeps bank balances. They have to be created in Umoja as new Business Partners with Treasury-related roles due to security and confidentiality requirements associated with transactions engaged by the UN Treasury. · Financial Services BP · UN Counterparty (Buyer or seller of the financial instruments) · UN Issuers (Issuer of the financial instruments) · UN Depository banks (Bank where custodial account is maintained) |
3.2.2 Summary Table of Business Partner Groups
|
Business Partner Grouping |
Group ID |
BP Number Range |
Source |
|
Third party: |
|||
|
Member States (Permanent Mission) |
Z011 |
1111XXXXXX |
OPPBA |
|
Non-Member State (Holy See etc.) |
Z012 |
12XXXXXXXX |
OPPBA |
|
Government and Local Authority |
Z013 |
13XXXXXXXX |
OPPBA |
|
UN Agency, Fund, Programme |
Z014 |
14XXXXXXXX |
OPPBA |
|
Inter Governmental and NGO |
Z015 |
15XXXXXXXX |
OPPBA |
|
Commercial: |
|||
|
Commercial Vendor (UNGM) |
Z010 |
111XXXXXXX |
UNGM (PD) |
|
Commercial Customer |
Z018 |
18XXXXXXXX |
OPPBA & UNGM |
|
Vendor (Non-UNGM) |
Z019 |
19XXXXXXXX |
OPPBA |
|
Individuals: |
|||
|
Individuals externals, Independent Contractors, Consultants, etc. |
Z016 |
20XXXXXXXX |
FPD & OHRM (Index#) |
|
Staff Member, Ex-Staff Member, Retirees, Survivors |
Z020 |
20XXXXXXXX |
OHRM (Index#) |
|
Non-Staff Military and Police |
Z021 |
20XXXXXXXX |
FPD (Index#) |
|
Treasury: |
|||
|
Treasury Partner |
Z017 |
17XXXXXXXX |
OPPBA (Treasury) |
3.2.3 Business Partner Roles
Each Business Partner belongs to one group, but can be assigned one or more roles. The BP role data is module-specific, such as UN Vendor data for Purchasing and Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) related processes and UN Customer data for the Sales and Distribution (SD) process. The roles ultimately determine how a Business Partner can be used in Umoja. Examples of business partner roles are as follows:
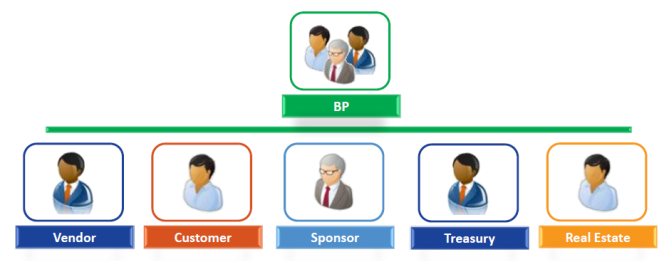
A vendor is a BP role to whom UN payments is made to. This role is needed before a BP can be used to procure goods and services, and send payments.
A customer is a BP role from whom invoices can be issued to and payments received from. This role is needed before a BP can be used for the provision of goods and services by the UN through the Umoja Sales & Distribution (SD) module, and billing and creating account receivables in the system.
A sponsor or donor, is a BP role that represents a government, institution or individual providing funding to UN. This role is needed before a BP can be used to record, track and report on grants-related transactions.
Multiple roles have been created for UN Treasury. These specialized roles need to be assigned to a BP before it can be used to execute treasury-related transactions and move funds.
· UN Financial Services BP
· UN Counter Party
· UN Issuer
· UN Depository Bank
Multiple roles have been created for Umoja Real Estate (RE) module. These specialized roles need to be assigned to a BP before it can be used to execute RE-related transactions. There are two distinct sets of Real Estate roles, one to be assigned to leases and the other to perform RE-related transactions within the system.
3.2.4 BP - Request for Creation or Update, Creation and Roles Assignment
A. Follow the process below to request for creation or an update to a BP:
A.1. Once the need to create or update a BP is identified, download the Master Data request form(s) from the Umoja iSeek homepage à Master Data Maintenance


A.2. Open the form and complete the required fields.

A.3. Send the completed form to umoja-mdm@un.org à an automated confirmation will be sent to the Requestor with a link to track progress.
A.4. Once the form has been received, the Reviewer will send an acknowledgement email to the Requestor.
A.5. A notification will be sent to the Requestor once the request is complete.
The following is an overview of the process to create a BP. Refer to the subsequent section for detailed steps:
1. Using the form that is submitted by the Requestor, the Master Data Maintainer determines the BP Grouping.
2. Next, based on the BP Grouping assigned, the Master Data Maintainer creates the BP as a general role. This is necessary for every BP record.
3. Using the table below, the Master Data Maintainer determines the required roles needed for the BP.
|
Business Partner Grouping |
Type of BP |
UN Vendor |
UN Low value vendor |
UN FI Vendor |
UN Customer |
UN Sponsor |
UN Financial services BP |
|
Third party: |
|||||||
|
Member States (Permanent Mission) |
Organization |
X |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
Non-Member State (Holy See etc.) |
Organization |
X |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
Government and Local Authority |
Organization |
X |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
UN Agency, Fund, Programme |
Organization |
X |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
Inter Governmental and NGO |
Organization |
X |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
Commercial: |
|||||||
|
Commercial Vendor (UNGM) |
Organization |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial Customer |
Organization |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
Vendor (Non-UNGM) |
Organization |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
|
Individuals: |
|||||||
|
Individuals externals, Independent Contractors, Consultants, etc.) |
Person |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Staff Member, Ex-Staff Member, Retirees, Survivors |
Person |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
Non-Staff Military and Police |
Person |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
Treasury: |
|||||||
|
Treasury Partner |
Organization |
|
|
|
|
|
X |
4. Using the form that is submitted by the Requestor, the Master Data Maintainer extends the relevant BP to the required BP roles and input all the essential and provided information.
5. The information is verified and approved by the Master Data Approver. If applicable, certain blocks are automatically or manually placed on the BP record until the information can be verified.
6. Once the information is verified, the BP record is unblocked and fully functional.
3.2.5 Business Partner Reconciliation Accounts
A BP Type that further categorizes the type of BP needs to be populated. This determines the reconciliation account that is automatically linked to the BP (for financial transactions).
|
Business Partner Grouping |
Group ID |
BP Type |
Recon Acct (Vendor) |
Recon Acct (Customer) |
|
Commercial Vendor - UNGM |
Z010 |
Z900 - Other Types |
0035101510 |
|
|
Commercial Vendor Non-UNGM |
Z019 |
Z900 - Other Types |
0035101510 |
|
|
Commercial Customer |
Z018 |
Z900 - Other Types |
|
0015101510 |
|
Staff member, Ex-Staff Member, Survivors |
Z020 |
Z001 - International Staff |
0035101610 |
|
|
Staff member, Ex-Staff Member, Survivors |
Z020 |
Z002 - Local Staff |
0035101610 |
|
|
Staff member, Ex-Staff Member, Survivors |
Z020 |
Z020 - Retiree |
0035101610 |
|
|
Non-Staff Military and Police |
Z021 |
Z004 - Military Staff Officer |
0035101710 |
|
|
Non-Staff Military and Police |
Z021 |
Z005 - Military Observer |
0035101710 |
|
|
Non-Staff Military and Police |
Z021 |
Z006 - UN Police |
0035101710 |
|
|
Individual External, Non-Staff - NO Payroll |
Z016 |
Z003 - UN Volunteer |
0035101810 |
|
|
Individual External, Non-Staff - NO Payroll |
Z016 |
Z100 - Individual Contractor |
0035101810 |
|
|
Individual External, Non-Staff - NO Payroll |
Z016 |
Z101 - Consultant |
0035101810 |
|
|
Member State |
Z011 |
Z900 - Other Types |
0033201010 |
0015101010 |
|
Non-Member State |
Z012 |
Z900 - Other Types |
0033201110 |
0015101110 |
|
Government & Local Authority |
Z013 |
Z900 - Other Types |
0035101210 |
0015101210 |
|
UN Agency, Fund, Programme |
Z014 |
Z900 - Other Types |
0035101310 |
0015101310 |
|
NGO and Intergovernmental |
Z015 |
Z900 - Other Types |
0035101410 |
0015101410 |
|
Treasury Partner |
Z017 |
Z900 - Other Types |
|
|
Thus, once a BP is created in the system and assigned a BP role e.g. Z018 Commercial Customer, the same BP number will be created automatically as customer in master record. The same attributes such as name, search term, address, contact number and other information in BP will be replicated in customer master record.

3.2.6 Business Partner Maintenance
The use of SAP Business Partner functionality is core to Umoja solution when processing transactions in ECC as well as SRM. Each module enables specific processes and requires the creation of Customer, Vendor and/ or BP.
BP Master Data Maintenance is an integrated Umoja solution spanning core modules in FI, TR, RE, GM, MM, and SD.
The following explains certain processes relevant to BP maintenance.
3.2.6.1 Create a New BP
B. The steps to create a new BP for Individual (i.e. Staff Member) / Transaction Code: BP
B.1. Enter BP in the Command field.
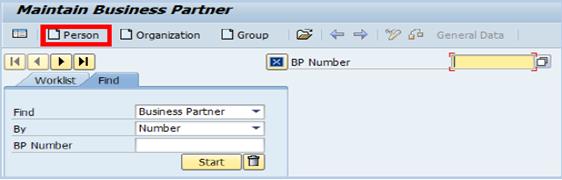
B.2. Click the Person button at the top of the main menu. -> the Create Person screen is displayed.
B.3. Select Business Partner (Gen.) from the Create in BP role drop-down list to create the generic profile for the BP

B.4. Select the corresponding group from the Grouping drop-down list. Make this selection based on the inputs specified on the form. Please take note that the BP grouping selected will control the assignment of BP number.
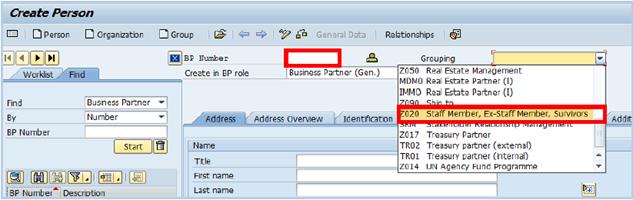
Note: For BP for Individual, the BP number will not be automatically generated. The User needs to manually enter the BP number, which is a 10-digit number starting with 20 and followed by the 8-digit index number of the individual.
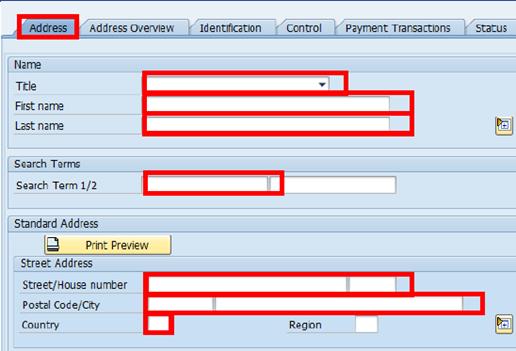
B.5. Click the Address tab and populate the following fields:
• Title: Select Mr. or Ms.
• First and Last name: This is the name of the BP that is being created.
• Search Term 1: Search Term is used as a method to conduct searching for a particular BP or group of BPs. This search term is the last name of the BP.
• Search Term 2: This search term is the first name of the BP.
• Street/House number: This represents the address of the BP.
• Postal Code/City: This represents the address of the BP.
• Country: This represents the address of the BP.
Note: All fields should be completed using CAPITAL LETTERS
B.6. Click on the Addit. Fields button to enter additional details on the BP.
B.7. Select an appropriate language from the Language match code list as the default language of communication with the BP in term of any system generated forms à press Enter.
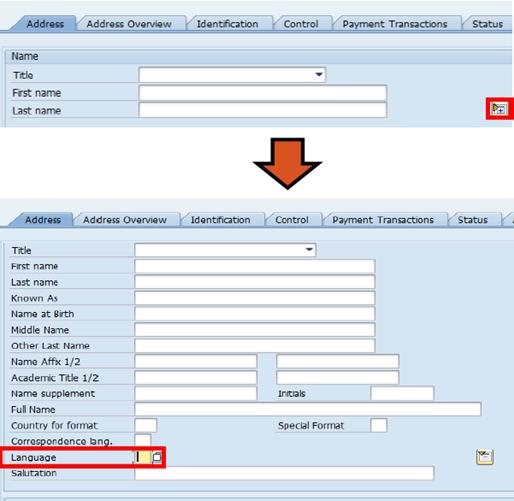
B.8. If applicable, additional addresses can be added for the newly created BP:
B.8.1. Click the Address Overview tab à click the Create button.
B.8.2. Populate the information in the pop-up window (as instructed previously) à click the Continue button.
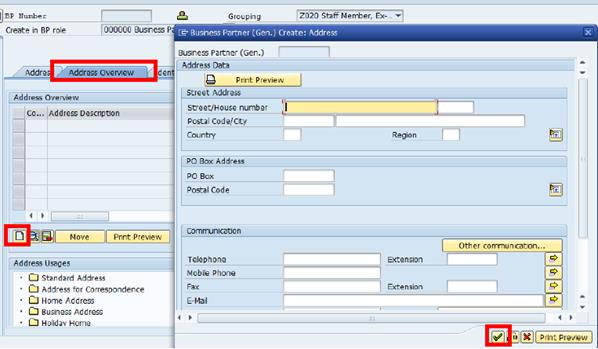
B.8.3. The additional address will appear as a second line à place the address in the correct Address Usage folder:
B.8.3.1. Double-click the appropriate folder, e.g. Address for Correspondence.
B.8.3.2. In the popup window, select the appropriate line item à click the Continue button.
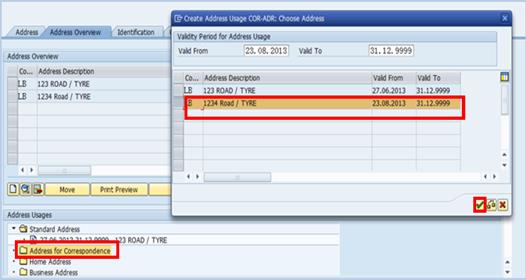
The additional address will appear in the corresponding folder:
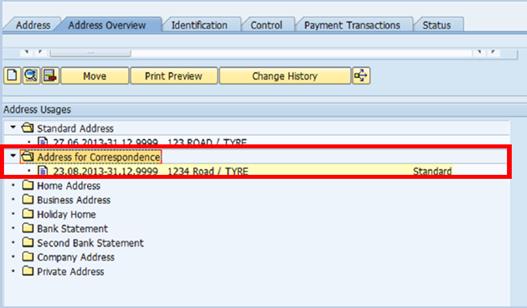
B.9. Click the Control tab to establish the BP Type and security Authorization Group for this BP record.
B.10. Click the match code icon in the BP Type field.
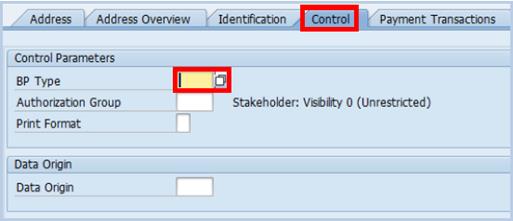
B.11. Select the appropriate BP Type code.
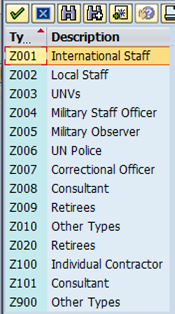
B.12. In the Authorization Group field, select the appropriate Authorization Group code (Z901). This will ensure that only authorized users for 'Individual' BP Group are allowed maintenance and approval accesses.

B.13. Click the Payment Transactions tab to add a new bank account.
B.14. Type the IBAN number in the IBAN field, if the BP has an IBAN number. The Switch Entry Type icon next to the IBAN field allows the user to type in free form. Note: This step can be skipped if the BP is paid by cash or cheque.
B.15. The bank account details are automatically populated in the Bank Details section.
B.16. Click the Generate Bank Details button.

B.17. If the BP does not have an IBAN number, enter the required details in the following fields:
• ID: a 4-digit field. The first 2 digits identify the type of the bank account (international or local) followed by a sequential number. Example: 1001 indicates the first local bank account.
· Ctry
• Bank Key
• Bank Account

Note: Make sure that relevant approval is received for any BP before following the next steps.
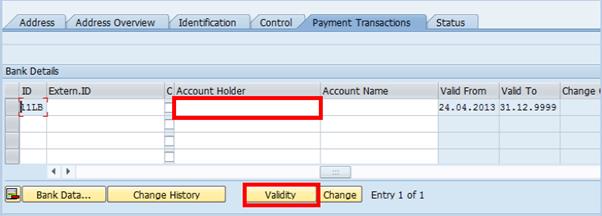
B.17.1. If the BP Name is different from Account Holder Name, enter the corresponding information in the Account Holder field.
B.17.2. Bank details should only be deleted if the information entered is incorrect. If bank details are being replaced with updated information, the old bank details should be set to expire by clicking the Validity button changing the Valid To date.
B.17.3. Save when complete.
3.2.6.2 Add a UN FI Vendor Role to BP for Individual
For BP's Staff Member and Non-Staff Military and Police, only UN FI Vendor Role should be assigned. This role is required to enable payment to these BP's.
C. Steps to add a UN FI Vendor role to a BP individual / Transaction Code: BP
C.1. Type BP in the Command field and click the Enter icon à the BP that was most recently processed will be displayed. If this is not the BP you want to add the Vendor role to, navigate to the appropriate BP.
C.2. Click the Display -> Change icon to make additional changes to the BP à select UN FI Vendor from the Change in BP role drop-down list.
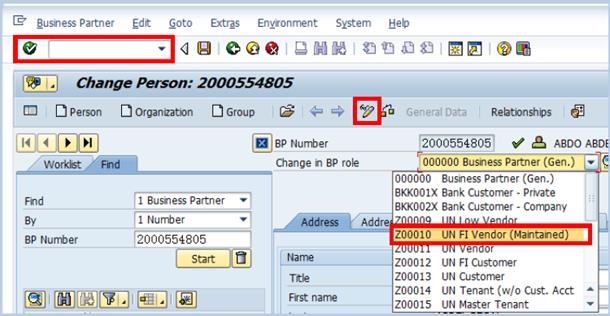
C.3. Additional tabs associated specifically with the UN FI Vendor Role for BP for Individual will appear but there is no compulsory field that need to be maintained:
• Employment Data
• Vendor: General Data
• Vendor: Tax Data
C.4. Review the information available in all the tabs, primarily the Address and Payment Transactions tabs. Most of the information in these tabs will be pre-populated from the generic BP profile.
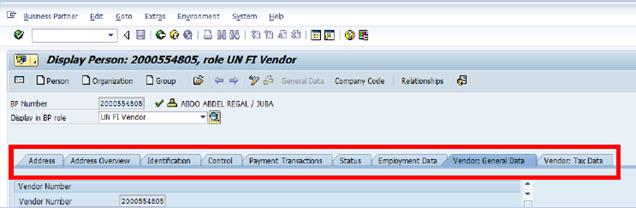
C.5. Click the Company Code view to add vendor-specific information à type 1000 in the Company Code field and click the Enter icon .

C.6. Click the Vendor: Account Management tab à review and ensure that the Reconciliation acct number assigned matches the BP Grouping type.
C.7. Type Z01 in the Sort key field and VI in the Planning group field à click the Enter icon.
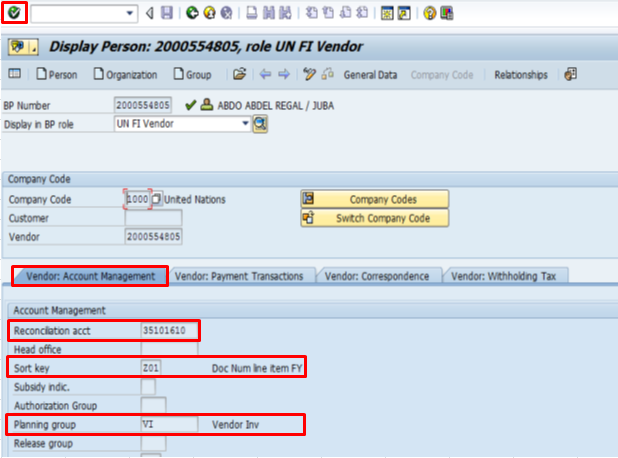
Note: The Sort key field indicates the layout rule for the Allocation field in the document line item and the Planning group field is used to determine the treasury cash flow.
The BP Group automatically determines the reconciliation account that is linked to the BP (for financial transactions).
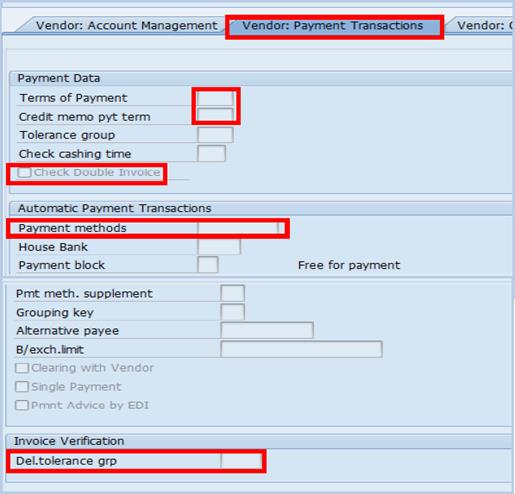
C.8. Click the Vendor: Payment Transactions tab à in both the Terms of Payment and Credit memo pyt term fields, type Z001 (paid immediately). Note that this is simply a default value and the information updated during the PO creation process can replace this information.
C.9. Select the Check Double Invoice check box.
C.10. Type an appropriate payment method code in the Payment methods field and Z001 in the Del.tolerance grp field à press Enter.
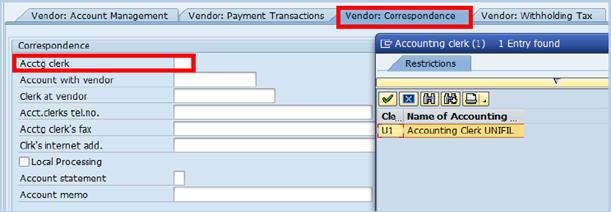
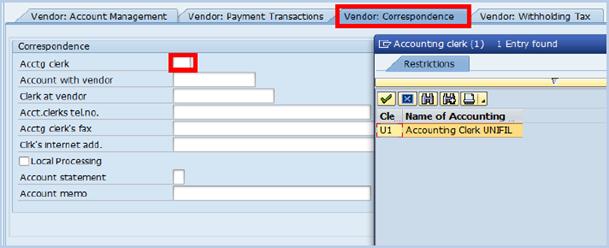
C.11. For cash/cheque payments (people without a bank account), the Accounting Clerk (Acctg clerk) field needs to be entered as an indicator as to which location this payment will be made à click the Vendor: Correspondence tab.
C.12. Type code correspondence to the location where payment by cash/cheque is expected in the Acctg clerk field and click Save when completed.
3.2.6.3 Change BP Grouping
BP Grouping can be changed for BP created for Individuals. This is because the BP Number ranges set for all 3 categories of the Individuals are set to be 20XXXXXXXX. BP Number will be maintained even if BP Grouping is changed. However, the Reconciliation Acct number will be changed automatically to match the new BP Grouping.
D. The steps to change the BP grouping for an existing BP (created for Individual) with UN Vendor Role / Transaction Codes: XK07, FK02 and BP
D.1. Type XK07 in the Command field and click the Enter icon.
D.2. Type the BP number in the Vendor field à a pop-up window appears on the screen. Ensure that the BP is selected.
D.3. Click the Enter icon.
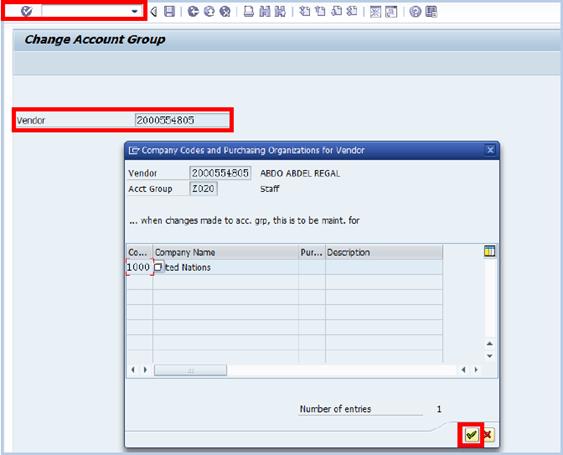
D.4. Enter the new account group for the selected BP in the New account group field --> click the Enter icon

D.5. If a BP group changes, the user also needs to change the BP's Reconciliation Account using the following steps:
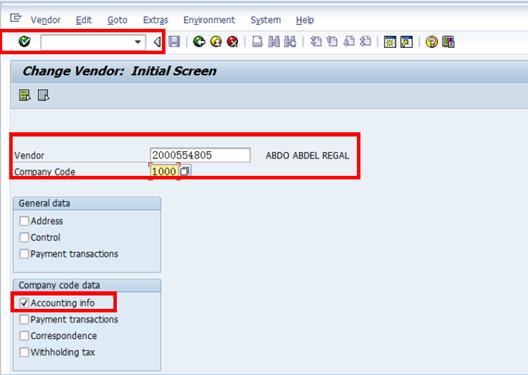
D.5.1. Type FK02 in the Command field and click the Enter Icon.
D.5.2. Enter the BP number and Company Code.
D.5.3. Select the Accounting Info check box à click the Enter icon.
D.5.4. Update the Recon. account number.
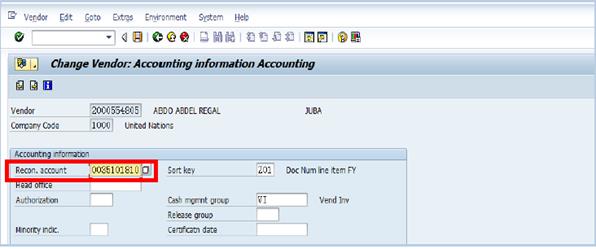
Note: The Recon. account number is the vendor account number. The Recon. account number for customers do not need to be updated. This is very important in ensuring that FI postings are correctly captured in the correct account.
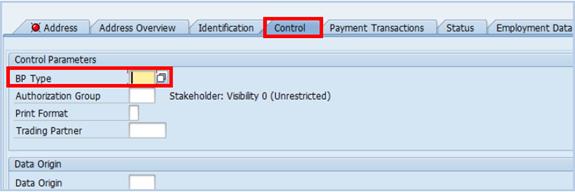
D.6. It is important to verify that the BP Type has been updated. Change the BP Type using following steps:
D.6.1. Type BP in the Command field and click the Enter icon à the BP that was most recently processed will be displayed. If this is not the BP you want to change BP Type, navigate to the appropriate BP.
D.6.2. Click the Display->Change icon to make additional changes to the BP à click the Control tab and change the BP Type to the appropriate one.
D.6.3. Save the BP when complete.
3.2.6.4 Add UN Vendor Role
BP for Individual Externals needs to be assigned UN Vendor Role and not UN FI Vendor Role. This is because payment to Individual Externals needs to be obligated through the Umoja SRM module using a special category of Purchase Orders (POs). By adding UN Vendor Role to these BP's, relevant purchasing information can be added for use by transactions related to Umoja SRM.
E. The steps to add a BP role to BP for Individual - vendor / Transaction Code: BP
E.1. Type BP in the Command field and click the Enter icon à the BP that was most recently processed will be displayed. If this is not the BP you want to add the Vendor Role to, navigate to the appropriate BP.
E.2. Click the Display->Change icon to make additional changes to the BP à select UN Vendor from the Change in BP role drop-down list.
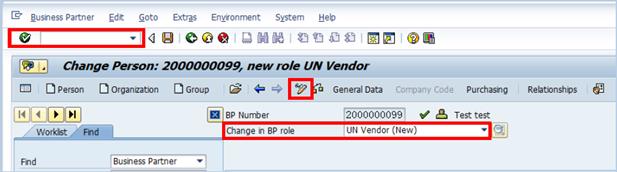
E.3. Review the information available in all the tabs, primarily the Address and Payment Transactions tab. Most of the information in these tabs will be prepopulated from the generic BP profile.
E.4. Additional tabs associated specifically with the UN Vendor Role will appear but there is no compulsory field that need to be maintained:
• Employment Data
• Vendor: General Data
• Vendor: Tax Data
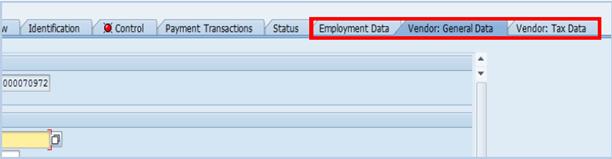
E.5. Click on the Company Code view to add vendor-specific information.
E.6. Enter 1000 in the Company Code field à press Enter.
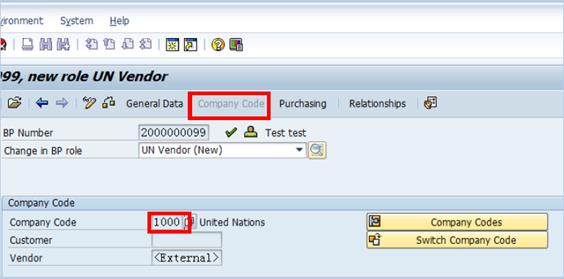
E.7. Click the Vendor: Account Management tab à review and ensure that the Reconciliation Account number assigned matches the BP Grouping type. (Note: The data in the Reconciliation acct (account) field is automatically populated based on the account group.)
E.8. Enter Z01 in the Sort key field and VI in the Planning group field à click the Enter icon.

Note: The data in the Reconciliation acct field is automatically populated based on the account group.
E.9. Click the Vendor: Payment Transactions tab à in both the Terms of Payment and Credit memo pyt term fields, type Z001 (paid immediately). Note that this is simply a default value and the information updated during the PO creation process can replace this information.
E.10. Select the Check Double Invoice check box.
E.11. Type an appropriate payment method code in the Payment methods field and Z001 in the Del.tolerance grp field à press Enter.
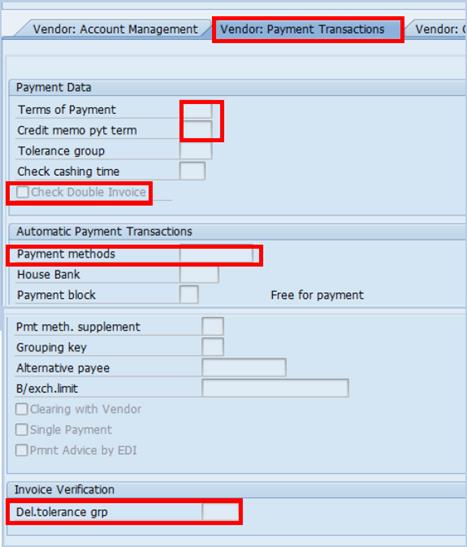
E.12. For cash/cheque payments (people without a bank account), the Accounting Clerk field (Acctg. clerk) needs to be entered as to which location this payment will be made à click the Vendor: Correspondence tab.
E.13. Code corresponding to the location where payment by cash/cheque is expected in the Acctg clerk field.
Note: Additional fields will be added in the future.
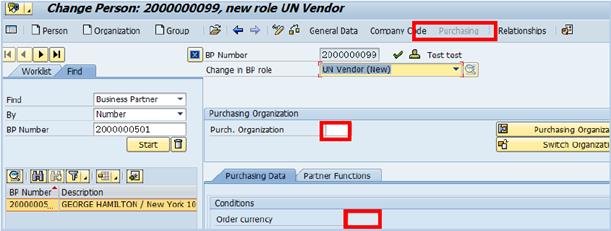
E.14. Click the Purchasing view button à type 1000 in the Purch. Organization field.
E.15. Enter the default Purchase Order (PO) currency in the Order currency field. Note that during the PO creation process, the information entered on the PO will override this currency.
E.16. In the Terms of Payment, type Z001 (paid immediately). Note that this is simply a default value and the information updated during the PO creation process can replace this information.
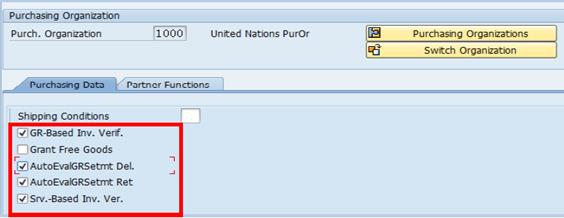
E.17. Scroll down and select the following check boxes:
· GR-Based Inv. Verif.: this ensures that a goods receipt transaction is performed against the PO. It is a default selection that can be removed from the document side.
· AutoEvalGRSetmt Del.: this is the electronic receipt settlement process that automatically creates an invoice when the goods receipt transaction takes place, e.g. services received for an individual contractor. This is used for the delivery of services.
· AutoEvalGRSetmt Ret: electronic receipt process used for the return of services (automatically reverse invoice).
· SRV-Based Inv. Ver.: this ensures that a service entry sheet (for service receipts) is performed against the PO.
E.18. Click the Save button à a warning box will appear with the message: 'Changes for vendor xxxxxxxxxx have not yet been confirmed. Display this message for this business partner again?' Note that this warning message will always appear prior to confirming a Vendor Role in the system.
E.19. Click the No button so that the message does not display again.
3.2.6.5 Deactivate/Expire a BP Role of a BP
To remove a role from BP, User has to either:
1. Deactivate or expire the relevant role by changing the role Valid To date (see F), or
2. Create a new BP without that particular role, block the old BP and link them together through 'Relationship' (see section 3.2.6.6).
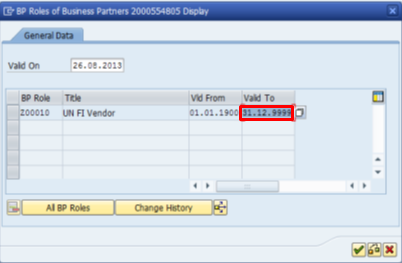
F. Steps to change the role Valid To date / Transaction Code: BP
F.1. Type BP in the Command field and click the Enter icon à the BP that was most recently processed will be displayed. If this is not the BP you want to add the Vendor Role to, navigate to the appropriate BP.
F.2. Refer to step C.2, click the Display -> Change icon to make additional changes to the BP à select BP role that need to be deactivate/expire from the Change in BP role drop-down list.
F.3. Click the Magnifying Glass icon, enter the Valid To date and hit Enter à click Save when complete.
3.2.6.6 Block/Unblock a BP
There are several methods and ways to block (or unblock) a BP from being used in performing transaction in the Umoja system:
· Central Block (T-code: BP) is used when a BP should no longer be used for any transactions in Umoja.
· Block/Unblock Vendor (T-code: XK05) is used when posting against and/or purchasing from the BP should be blocked.
· Sales Block (T-code: BP) or Customer Block/Unblock (T-code: XD05) is used when all or certain Sales and Distribution (SD) related transactions should no longer be performed against the BP.
Note: Before blocking a BP, the user needs to check for pending invoices.
G. The process to do a central block / Transaction Code: BP
G.1. Type BP in the Command field and click the Enter icon.
G.2. In the BP Number field, enter the relevant BP number that needs to be blocked.
G.3. Click the Display -> Change icon to make additional changes to the BP.
G.4. Click the General Data button.
G.5. Click the Status tab.
G.6. Select or Unselect the Central Block check box under the Lock section to lock the BP.
G.7. Click the Save icon.
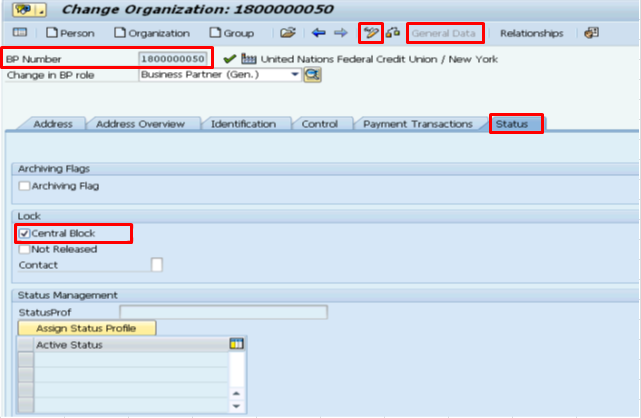
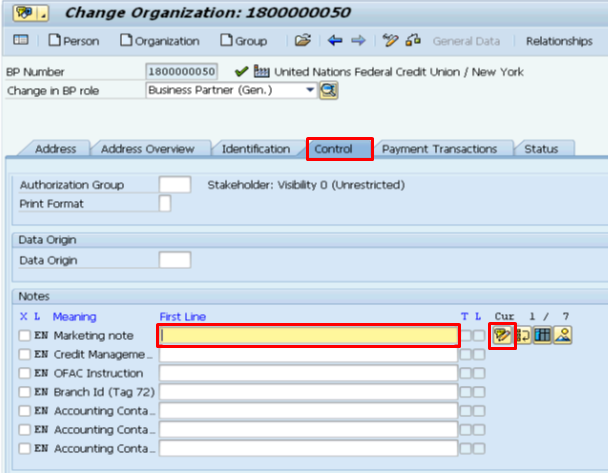
G.8. It is not possible to include any note directly against the Central Block check box at the Status tab. Any note the user wants to add to the BP shall be entered in the Notes field at the Control tab.
G.9. Go to the appropriate note field.
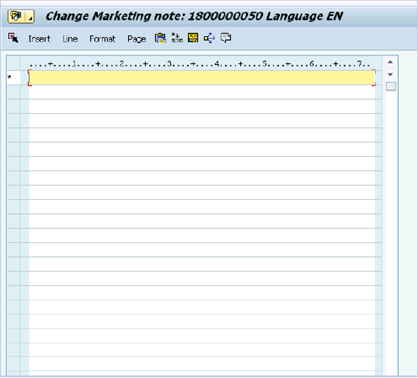
G.10. Click the Pencil icon and enter relevant information in the text field.
G.11. Click the Save icon when completed.
H. The process to block / unblock Vendor / Transaction Code: XK05
H.1. Type XK05 in the Command field and click the Enter icon.
H.2. Type the appropriate BP number in the Vendor field.
H.3. Type 1000 in the Company Code and the relevant Purch. Organization (if need to be specified) in the provided fields à click the Enter icon.
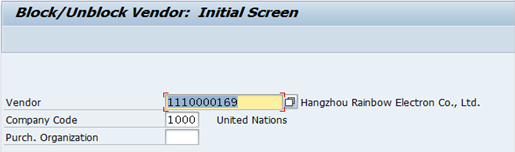
H.4. Select or unselect the appropriate check boxes in the Posting Block, Purchasing Block and Block for quality reasons sections to block the vendor functions à click the Save icon.

I. The process to do sales block/unblock / Transaction Code: BP
To block (or unblock) a BP with UN Customer role from any Sales and Distribution (SD) related transactions.
I.1. Type BP in the Command field and click the Enter icon.
I.2. In the BP Number field, enter the relevant BP number that needs to be blocked.
I.3. Click the Display -> Change icon to make additional changes to the BP.
I.4. Click the Sales and Distribution button à click the Status tab.
I.5. Select or unselect the appropriate Sales Block check box à click the Save icon.
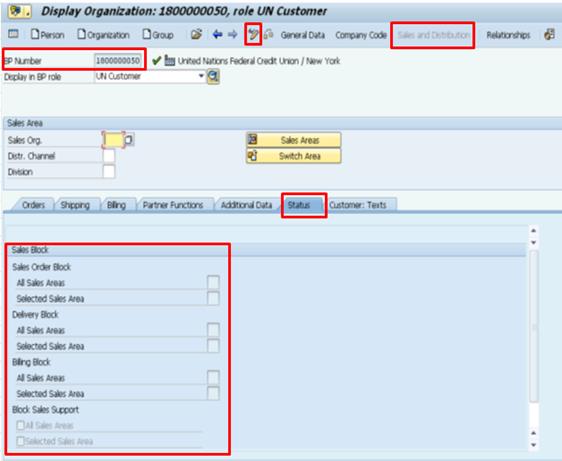
I.6. Click the Company Code button à click the Customer: Status tab.
I.7. Select or unselect the appropriate Posting Block check box à click the Save icon.
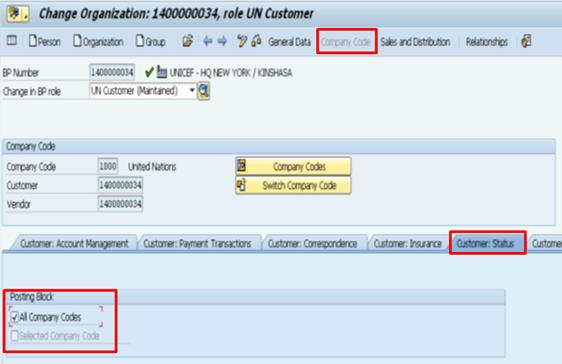
J. Alternatively, use T-code XD05 to block or unblock the Sales and Distribution (SD) related functions of the BP / Transaction Code: XD05
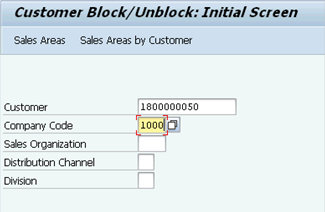
J.1. Type XD05 in the Command field and click the Enter icon.
J.2. Type the appropriate BP number in the Customer field.
J.3. Type 1000 in the Company Code and the relevant Sales Area (if need to be specified) in the provided fields à click the Enter icon.
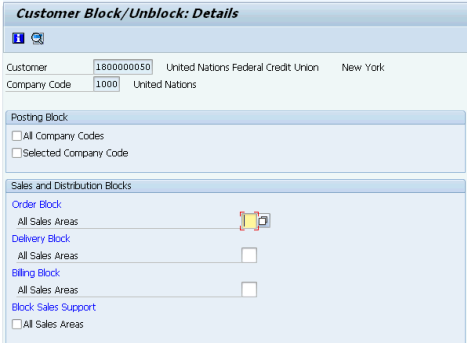
J.4. Select or unselect the appropriate Posting Block and/or Sales and Distribution (SD) Blocks check boxes à click the Save icon.
3.2.6.7 Add Alternate Payee
Alternate Payees can be added to a Vendor Role, e.g. to receive invoice against one vendor and pay another vendor.
K. Steps to add alternate payee / Transaction Code: FK02
K.1. Type FK02 in the Command field and click the Enter Icon.
K.2. Enter the BP number and Company Code.
K.3. Select Payment transactions --> click Enter.
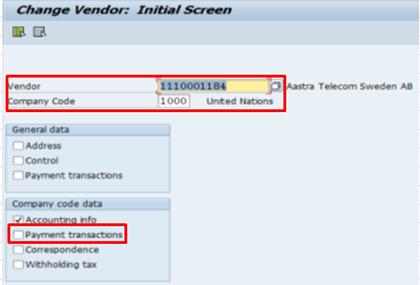
K.4. Check the Individual spec. box
K.5. Click on the Permitted Payee button. Enter the BP number of the alternate payee.
K.6. Save the record when completed.
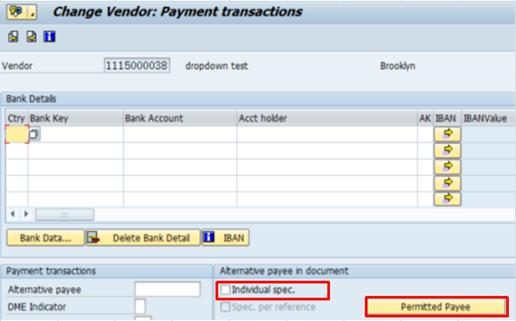
L. Alternatively, use T-code BP to add alternate payee / Transaction Code: BP
L.1. Type BP in the Command field and click the Enter icon.
L.2. Enter the relevant BP number in the BP Number field.
L.3. Click the Display -> Change icon to make additional changes to the BP à select the BP role (UN FI Vendor or UN Vendor) from the Change in BP role drop-down list.
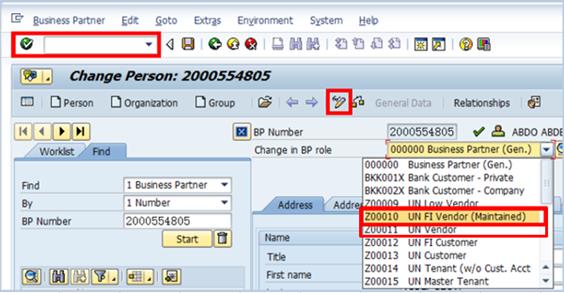
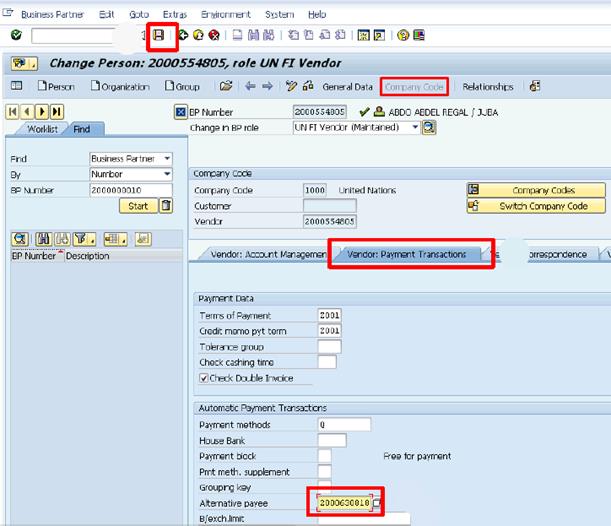
L.4. Click the Company Code option à select the Vendor: Payment Transactions tab.
L.5. Enter the BP number of the alternate payee in the Alternative payee field à click the Save icon.
3.2.6.8 Terminate a BP
If a BP is no longer active or its relationship with the UN has ended, the BP can be terminated.
M. Steps to terminate a BP / Transaction Code: BP
M.1. Type BP in the Command field and click the Enter icon.
M.2. Enter the relevant BP number in the BP Number field.
M.3. Click the Display -> Change icon to make additional changes to the BP à click the General Data and going to the Status tab.
M.4. Populate the followings:
· Check the Archiving Flag
· Check the Central Block
· Enter the End Date
· Enter the date in the Customer Last Contact field
M.5. Click Save.
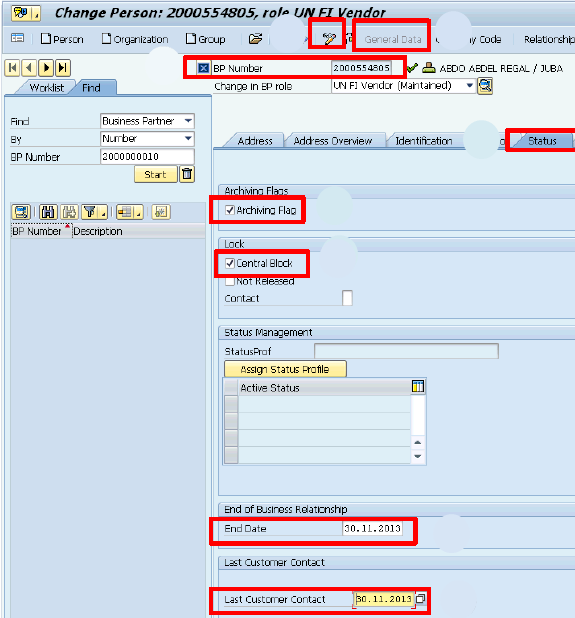
3.2.6.9 Approve a BP (Vendor)
The T-codes used for approving a BP in Umoja are as follows:
|
Approve |
T-code |
|
Vendor BP |
FK08 |
|
Multiple Vendor BP changes |
FK09 |
N. The steps to approve a vendor / Transaction Code: FK08
N.1. Type FK08 in the Command field and click the Enter icon.
N.2. Type the vendor BP number in the Vendor field.
N.3. Type 1000 in the Company Code field à click the Enter icon.
N.4. BP Approver (no bank data): Click the Changes to Sensitive Fields button at the central level and company code level to review all changes, if the Current status field shows the status To be Confirmed. If the Current status field shows the status as Confirmed, then there are no changes that need to be confirmed.
N.5. BP Approver (with bank data): Click the Changes to sensitive fields button at the company code level and review all changes, if the Current status field shows the status To be Confirmed. If the Current status field shows the status as Confirmed, then there are no changes that need to be confirmed.
N.6. Click the Confirm or Refuse button after reviewing the changes at the central or company code level à click the Save icon.

O. The steps to approve multiple vendor BP changes / Transaction Code: FK09
O.1. Type FK09 in the Command field and click the Enter icon.
O.2.
Type the vendor range in the relevant Vendor fields à click the ![]() icon.
icon.
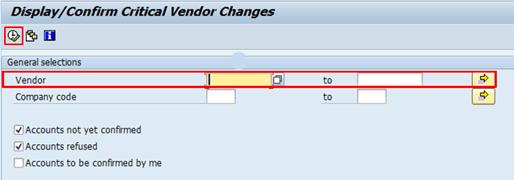
O.3. The following screen will appear, listing BP's with vendor roles that require confirmation.
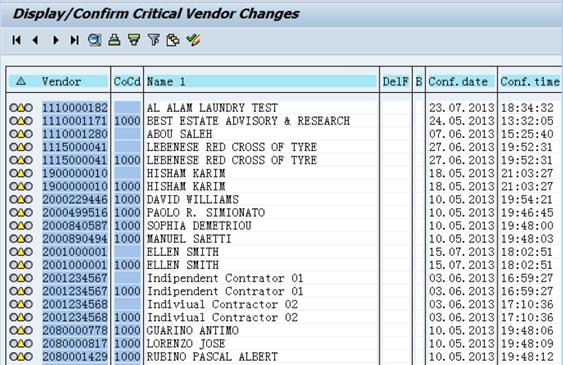
O.4. Click on each active link to open the Confirm Change Vendor screen and confirm the status change of each record.
4 Umoja Coding Block
4.1 Introduction to Coding Block
The Umoja Coding Block is a tool that provides the following:
· Describes the data structure for recording financial transactions.
· Is used for revenue and expense financial transactions.
· Is comprised of coding block elements that provide different financial views.
· Allows the user to populate only required fields (that is, to 'derive' related fields).
In Umoja, each module maintains a ledger and generates documents that make use of the coding block elements. These ledgers work in sync so that when a user posts a transaction in one ledger, corresponding entries are created in the other three. The four main ledgers of Umoja are as follows:
· General Ledger (maintained in the FI module): The GL only records actual postings. Every financial transaction conducted in Umoja has a corresponding posting within the GL.
· Controlling Ledger (maintained in the CO module): The Controlling Ledger records postings used for cost and management accounting.
· Funds Management Ledgers (maintained in the FM module): The FM Ledgers record budget-relevant transactions, such as budget, consumption, budgetary resources, etc. and provides budget availability.
· Grants Ledger (maintained in the GM module): The Grants Ledger records grant-relevant transactions.
Each of the finance-related module stores data differently. This provides flexibility to perform different analysis within modules. To ensure that data remains consistent across the organization, Umoja automatically links data elements across modules:
· Umoja uses the concept of 'Simultaneous Posting' for transactions in one module to be automatically posted in all other corresponding ones; and
· This provides a control point so that if a transaction does not post simultaneously in all modules, then the transaction will fail and prompt the user with an error message.

In Umoja, a functionality called 'Derivation' is used to extract the linked account assignments with a minimal entry of coding block elements during transaction entry. For example, Cost Center will always derive the Business Area, Functional Area, Funds Center and Profit Center. When a User conducts a transaction requiring all such fields, only the Cost Center has to be entered the other fields are automatically populated.

As an illustration, using transaction code FB60 - create an AP invoice, the business user will enter the following values:
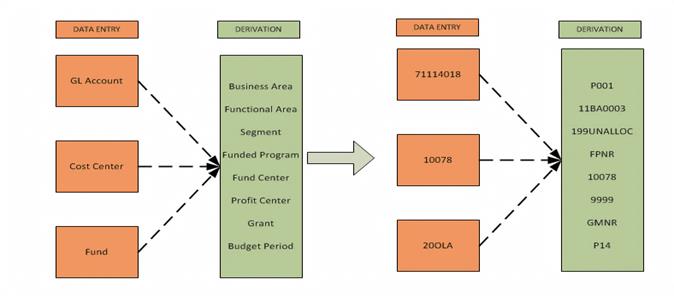
Below is the graphical presentation of Umoja Coding Block derivation by highlighting what master data elements are entered in FI, and derived across four ledgers based on business transactions posted in Umoja.
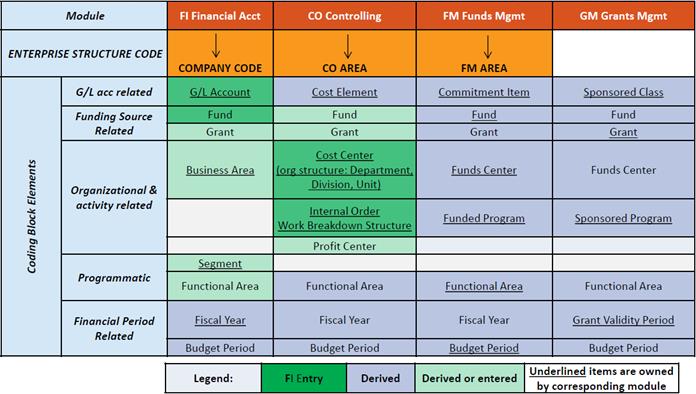
The Umoja Coding Block design including derivation is based on UN reporting and analysis requirements to ensure the transactions processed are grouped and rolls up to the UN reporting structure. Below is the mapping of UN classification requirements to coding block data elements.
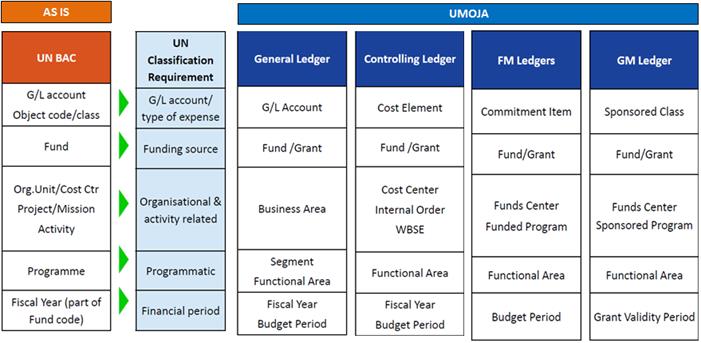
'In Umoja, there are a number of changes using the Umoja Coding Block and the simultaneous postings in General Ledger, Controlling Ledger, Funds Management Ledger, and Grants Ledger:
· Accrual accounting is adopted for financial accounting purposes;
· General Ledger is used for IPSAS actuals only;
· Controlling Ledger is used to support managerial accounting;
· Umoja has defined additional cost centers to support results-based management in the long-term;
· Funds Management Ledgers are used for budgetary control and are on cash basis;
· Functional area is used for more detailed programmatic analysis;
· Grants Ledger is used to track individual donor contributions and is on cash basis;
· Data will be entered in Umoja environment only;
· Business processes will be more automated; and
· Data will be stored in one central data repository across the UN Secretariat.
4.2 Umoja Coding and Naming for Individual Coding Block Element
4.2.1 GL Account
· Code length: 8 characters
· Code composition: numeric smart code
· Short text: max. is 20 characters
· Long text: max. is 50 characters
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
Type* |
Group |
sub-group |
specific code |
||||
|
7 |
410 |
10 |
30 |
||||
*Type:
|
1 |
Current Assets |
|
2 |
Non-Current Assets |
|
3 |
Current Liability |
|
4 |
Non-Current Liability |
|
5 |
Net Assets |
|
6 |
Revenues |
|
7 |
Expenses |
|
8 |
OFF Financial Statements / Memo |
Example of a GL account
|
GL Acct |
Short Text |
Long test |
|
11011010 |
Csh HQ USD Nominal |
Cash HQ New York JPMorgan USD Wire ACH Nominal |
Example of GL accounts for accounts receivable
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
Type |
Group |
sub-group |
specific code |
||||
|
1 - Current |
410 - Assessed 411 - Voluntary 510 - Exchange 520 - VAT |
10 - Member State 11 - Non-Memb State 12 - Govt & Local Authority 13 - UN Family 14 - Intergovt & NGO 15 - Commercial 16 - Staff, Retirees 17 - Military & Police 18 - Individuals Extern |
10 Control Acct 14 Manual Reclassificat. 16 Allowance (AFDA) 19 Revaluation |
||||
4.2.2 Sponsored Class
· Code length: 20
· Code composition: alpha-numeric
· Short Text / Description: max. is 30 characters
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
.. |
.. |
.. |
19 |
20 |
|
series |
dash |
description of sponsored class |
||||||||
|
AR1 |
- |
TRAVEL |
||||||||
|
AR1 |
- |
Contract Service |
||||||||
|
AR1 |
- |
Vol Contr Cash |
||||||||
4.2.3 Fund
· Code length: 5 characters
· Code composition: alpha-numeric code that includes the fund type
· Short Text / Description: max. is 20 characters; current fund names need to be shortened
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
numeric fund type number |
alpha code |
|||
|
10 |
UNA |
|||
Example:
|
Fund Code |
Fund Description |
|
10UNA |
UN General Fund |
|
10WCA |
Working Capital Fund |
4.2.4 Grant
• Code length: 15
• Code composition: alpha-numeric
• Grant Type alpha-numeric:
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
|
Grant type |
- |
Fund |
- |
Sequential number |
||||||||||
|
S1 |
- |
32FSA |
- |
0 0 0 0 0 1 |
||||||||||
|
R1 |
- |
32CER |
- |
0 0 0 0 0 2 |
||||||||||
· Grant types will be created for major categories: S1 - Simple Grant, R1 - Resource Mobilization Grant, M1 - Main Implementation Grant, and P1 - Passthrough Grant
· Short Text / Description: max. is 20 characters
4.2.5 Business Area
• Code length: 4 characters
• Code composition: alpha-numeric smart code
• Description: max. 30 characters
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
group, numeric |
sub-group, numeric, (zero-fill) |
||
|
S |
10 |
1 |
|
Example:
|
Code |
BA Description |
|
S101 |
United Nations Headquarters |
|
S201 |
UN Office at Geneva |
|
F400 |
UNODC |
|
S101 |
UN Treasury Pools |
4.2.6 Cost Center
· Code length: 5
· Code composition: sequential number* (starting with 10000)
· Short text/description: max. is 20/40 characters; current org. unit names need to be shortened
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
sequential number |
||||
|
10029 |
||||
Example:
|
10029 |
UNON Chief HRMS |
|
10030 |
UNON Staff Admin Sct |
4.2.7 Fund Center
• Normal Fund Centers: see cost center code
• High-level Fund Centers: 6-14 characters, alpha-numeric, prefix to identify where budget is entered and spending is controlled
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
|
Prefix 'B' |
_ |
Cost/Fund Center Group Code |
||||||||||
|
Department/entity abbreviation |
seq. number |
|||||||||||
|
B |
_ |
UNOG |
001 |
|||||||||
Example
|
10021 |
Central Accounts Sec |
|
10022 |
PK Accounts Section |
|
BC_UNON.001 |
UNON Adm of Justice |
|
BC_UNON.003 |
UNON HRM Service |
4.2.8 Internal Order
· Code length: 8
· Code composition: sequential number, because the attribute Business Area and Responsible Cost Center will link the Internal Order to an Organizational Element
· Short Text / Description: max. is 40 characters
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
Order Type |
sequential number |
||||||
|
11 |
0 0 0 0 0 1 |
||||||
Example
|
10000080 |
ZM09 - Service Order (internal client/ department) |
|
6000016 |
CS02 - Billable Service Order |
|
12000000 |
1200 - PK assessed contribution in kind |
|
19000024 |
1920 - GM passthrough orders |
4.2.9 Project/WBSE
· Code length: 18
· Code composition: alpha-numeric, the first 9 characters composing the project identifier, the rest is used for the project structure
· Description: max. is 40 characters
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
|
project code |
- |
sequential number |
seq no |
seq no |
seq no |
||||||||||||
|
AA |
- |
0 0 0 0 4 5 |
0 1 |
0 1 |
0 1 |
||||||||||||
Example
|
AA-000005 |
Office Facility |
|
AA-000005.01 |
Design |
|
AA-000005.02 |
Construction |
|
AA-000005.03 |
PMO |
4.2.10 Funded Program
· Code length: 11-18 characters
· Code composition: alpha-numeric
· Short Text / Description: max. is 20 characters
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
.. |
.. |
.. |
.. |
16 |
17 |
18 |
|
project code or 'IO' |
- |
Internal Order code or Project code |
|||||||||
|
AA |
- |
0 0 0 0 4 5 . 0 1 . 0 1 . 0 1 |
|||||||||
|
IO |
- |
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 |
|||||||||
('IO' for Internal Orders)
Example
|
AA-000005 |
Office Facility |
|
AA-000005.03 |
PMO |
4.2.11 Sponsored Program
· Code length: 10
· Code composition: alpha-numeric
· Short Text / Description: max. is 30 characters
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
Earmarking |
- |
sequential number |
|||||||
|
F 0 1 |
- |
100001 |
|||||||
Example
|
Sp Prgr Code |
Description |
|
F01-100123 |
Vaccination Africa |
4.2.12 Profit Center
• Code length: 4 characters
• Code composition: sequential number, with a CO Profit Center hierarchy to create service lines
• Short Text / Description: max. is 20 characters
Examples
|
Code |
Short Text |
|
1001 |
Audit |
|
1002 |
Legal |
|
1003 |
Safety and Security |
4.2.13 Functional Area
· Code length: 7, plus 5 for RBM
· Code composition: numeric
· Short Text: max. is 25 characters, current programme names have to be shortened
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
|
program code |
categ |
group |
sub-programme |
sub-activity |
budget period (optional) |
result (optional) |
|||||||||
|
1 1 |
A |
A |
1 2 3 4 |
1 2 3 |
B 1 3 |
0 1 |
|||||||||
Example
|
Code |
Description |
|
12AZ0007 |
NB funct control |
|
12AA0007 |
Exec Dir Mgmt NB |
|
12AC0007001 |
SP PPBA Nairobi |
|
12AC0007002 |
SP HR Nairobi |
|
12AC0007003 |
SP Supprt services NB |
|
12AC0007004 |
SP ICT ops NB |
4.2.14 Budget Period
· Code length: 3-4
· Code composition: alpha-numeric
· Description: max. is 35 characters
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
(4) |
|
code |
year |
'E' |
|
|
B |
1 3 |
||
Code: B = biennium, A = annual, P = peace keeping, MYn = multi-year
Character 4: E = peacekeeping extended
4.3 Document Posting
Document: An accounting document consists of a header and line items. Header is the part of a document that contains information valid for the whole document, for example document date, posting date, document type and document number.
Document type is a key that is used to classify accounting documents and differentiate the nature of business transactions to be posted. The system usually defaults the appropriate document type when a business transaction is entered. The document type determines which account types such as vendor, customer, materials, asset, and normal GL accounts can be posted to. A separate number range is assigned to every document type. In Umoja, both standard and custom document types are used.
Attached is the list of document types which are used in Umoja. Please take note that the list is subject to change based on business requirements identified by the UN.
Posting Keys are synonymous to debit and credit side of accounting entries however apart from this; it also determines the account type to be used at debit and credit lines.
December, 2016
