Document_GEM: Development Issues Series
Development Issues Series
1 August 2017
Summary: In June 2017, the Fed raised its key policy rate for the fourth time since December 2015, and announced plans to gradually reduce the size of its balance sheet. Amid high economic and policy uncertainty, however, rising interest rates by the F ...
21 April 2017
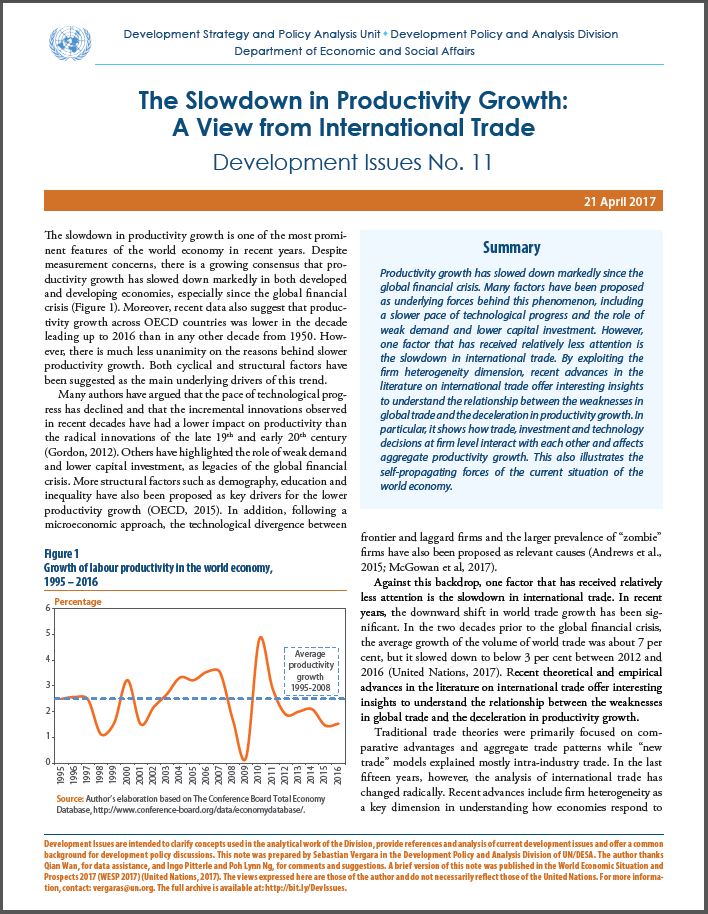
Trade, investment and technology decisions at firm level interact with each other and affects aggregate productivity growth. This also illustrates the self-propagating forces of the current situation of the world economy.
24 March 2017
A review of recent trends suggests the need for a renewed commitment and enhanced efforts by the international community to support financing for sustainable development. It also points out at potential risks of debt sustainability for a few developed and some emerging economies.
2 March 2017
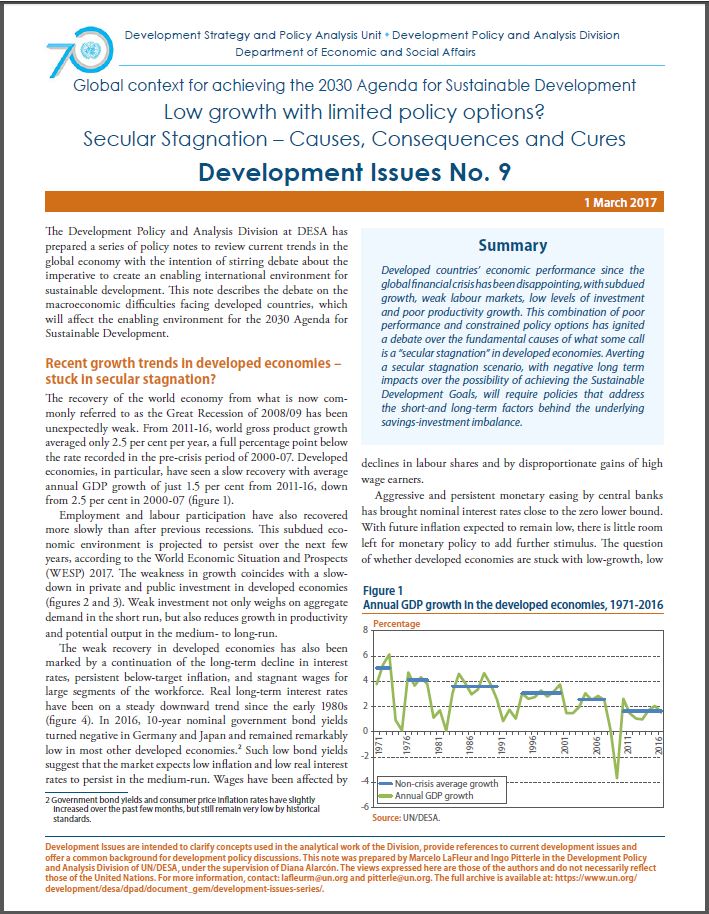
Summary: Developed countries’ economic performance since the global financial crisis has been disappointing, with subdued growth, weak labour markets, low levels of investment and poor productivity growth. This combination of poor performance and const ...
27 February 2017
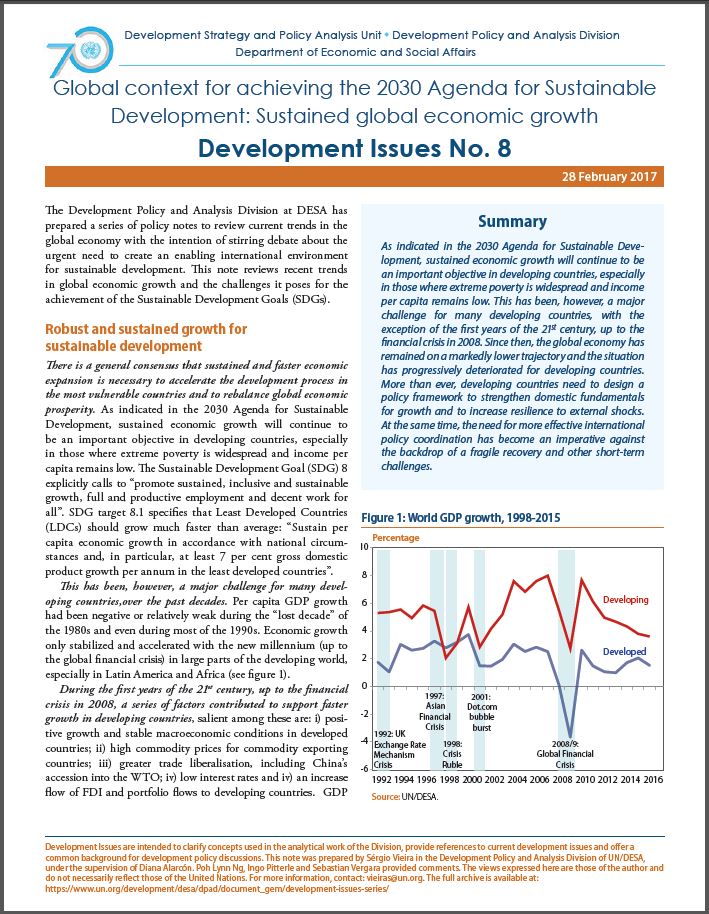
Summary: As indicated in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, sustained economic growth will continue to be an important objective in developing countries, especially in those where extreme poverty is widespread and income per capita remains lo ...
13 February 2017
The global economy remains trapped in prolonged episode of slow growth, of which weak international trade is both a cause and a symptom. While developing countries have become more integrated and benefitted from international trade in recent years, this has also made them more vulnerable to a slowdown in global trade. Ensuring an enabling global environment for trade is thus critical for progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals, in particular given the risks associated with protectionism and inward-looking policies, which is on the rise in many countries.
2 January 2017
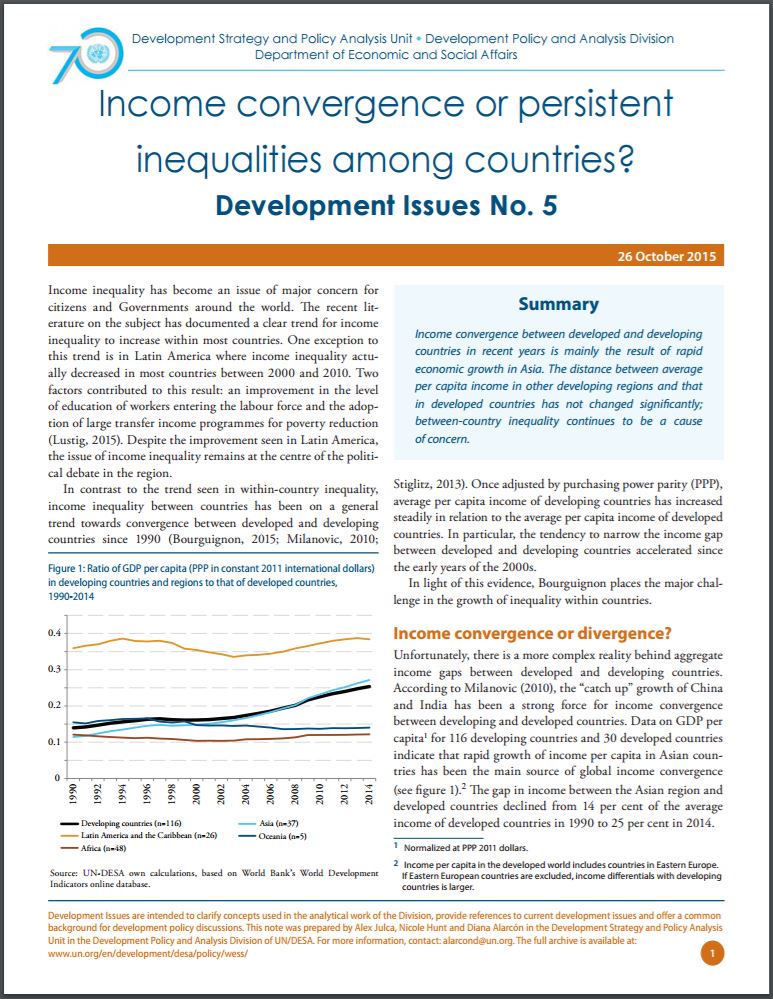
Income convergence between developed and developing countries in recent years is mainly the result of rapid economic growth in Asia. The distance between average per capita income in other developing regions and that in developed countries has not chan ...
26 October 2015
Income convergence between developed and developing countries in recent years is mainly the result of rapid economic growth in Asia. The distance between average per capita income in other developing regions and that in developed countries has not changed significantly; between-country inequality continues to be a cause of concern.
21 October 2015
The subject of inequality appears throughout the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, both directly and indirectly. When examined across the four different angles of inequality—access, gender, opportunity and outcomes—many goals and targets of the Sustainable Development Goals are clearly linked to inequality.






Follow Us