
World Economic Situation and Prospects: April 2024 Briefing, No. 180
 Debt Sustainability Challenges in Africa: The Role of Domestic Debt
Debt Sustainability Challenges in Africa: The Role of Domestic Debt
In 2024, more low-income countries are facing debt distress or are at risk of debt distress than ever before. According to the latest IMF low-income countries debt sustainability analysis, 10 countries are in debt distress, while 52 countries are at moderate or high risk of debt distress. Out of these 62 countries, 40 are in Africa. African countries have suffered gravely from global shocks such as the COVID-19 pandemic, the war in Ukraine and spillover effects of high interest rates in many developed countries, which have increased debt levels across the continent. Debt levels are particularly high in the continent’s larger lower middle-income economies, including Egypt at 92 per cent of GDP, Angola at 84.9 per cent, and Kenya at 70.2 per cent.
 For many African countries, the growing debt levels and associated high debt servicing costs are an impediment to long-term sustainable economic growth prospects. Revenues have also not kept up with expenditure needs. In sub-Saharan Africa, average government revenue declined from 19.7 per cent of GDP in 2010 to 17.5 per cent in 2023. Shrinking revenues in the face of higher debt servicing costs further limit the scope for public expenditures, setting back progress towards the SDGs while increasing pressures for additional borrowing.
For many African countries, the growing debt levels and associated high debt servicing costs are an impediment to long-term sustainable economic growth prospects. Revenues have also not kept up with expenditure needs. In sub-Saharan Africa, average government revenue declined from 19.7 per cent of GDP in 2010 to 17.5 per cent in 2023. Shrinking revenues in the face of higher debt servicing costs further limit the scope for public expenditures, setting back progress towards the SDGs while increasing pressures for additional borrowing.
Whether debt is external or domestic can be assessed along three criteria: currency of issuance, the governing jurisdiction, or residence of debt holders. Domestic debt can therefore be described as debt which is issued in the sovereign’s local currency, or debt which is governed by the domestic sovereign laws. It can also be defined as debt which is held by residents of the issuing sovereign.
Most African countries have historically relied on external debt in the form of long-term concessional financing from multilateral and bilateral lenders, or non-concessional private finance. However, in efforts to diversify financing sources and reduce risks of external debt vulnerabilities, many countries have increasingly turned towards domestic debt markets over the past two decades, reflecting a trend seen more broadly across developing countries. In emerging markets and developing economies, on average, domestic debt made up approximately 58 per cent of debt in 2022 and accounted for approximately 66 per cent of government debt accumulation since 2010.
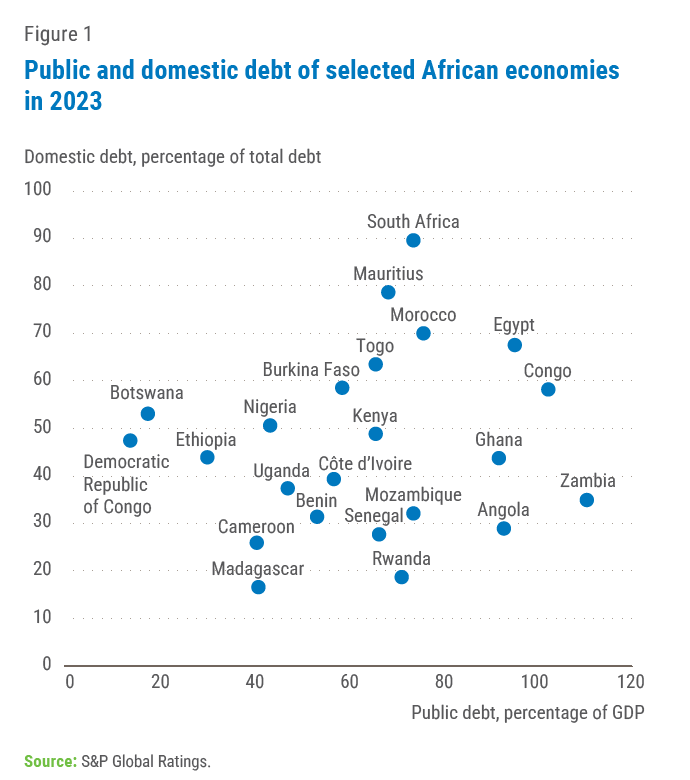
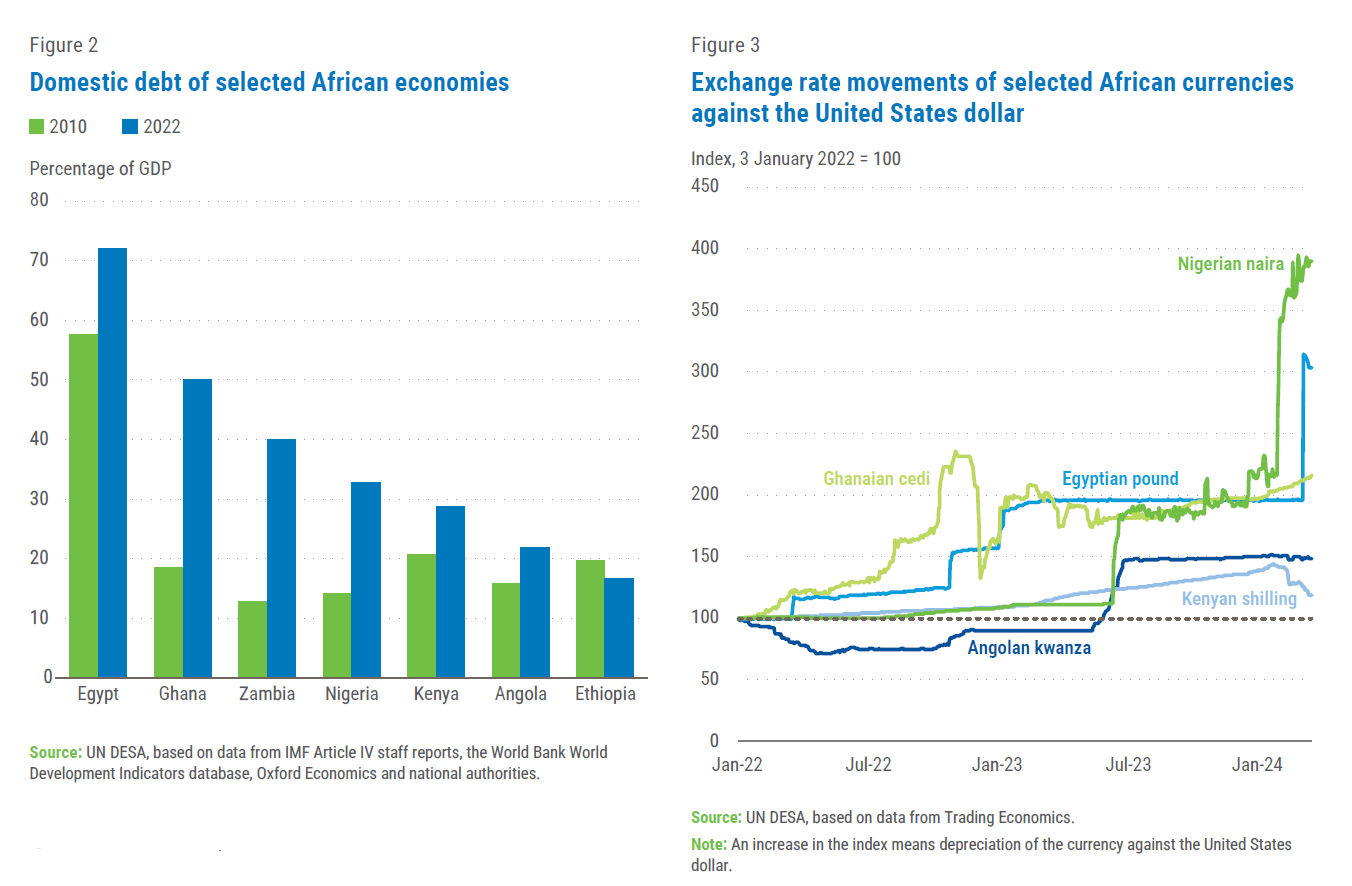
Domestic debt has, however, presented a new set of challenges on debt sustainability. The S&P Global Africa Domestic Debt Vulnerability Index ranks Egypt, Ghana, Kenya, Mozambique, Angola and Zambia among the most vulnerable countries as of 2023. Due to limits in data availability, subsequent data analysis in the brief will focus largely on these countries. Figure 1 shows the total public debt in selected countries, with the corresponding share of domestic debt. Figure 2 shows the trend in domestic debt accumulation in the selected countries.
Potential benefits derived from domestic debt in Africa
Most of the domestic debt in Africa is denominated in local currencies and is therefore shielded from exchange rate volatility and currency mismatches. Since 2022, a number of African currencies recorded significant depreciation against the US dollar as shown in figure 3. Currency depreciation leads to an increase in foreign currency-denominated external debt. In Kenya for instance, as of December 2023, external debt – 67.3 per cent of which was dollar denominated – increased by $1.3 billion owing in part to depreciation of the Kenyan shilling. As well, approximately 98 per cent of Ghana’s external debt stock growth in 2023 was a result of the cedi’s depreciation against the dollar. Nigeria’s external debt in 2023 also increased by 100.1 per cent over a year because of the naira’s depreciation. Avoiding sharp and unexpected depreciation of domestic currencies can ensure that governments maintain predictability on domestic debt stock and movements. In addition to this, issuance of debt in domestic currency grants central banks and governments flexibility to employ monetary policy tools in domestic debt management.
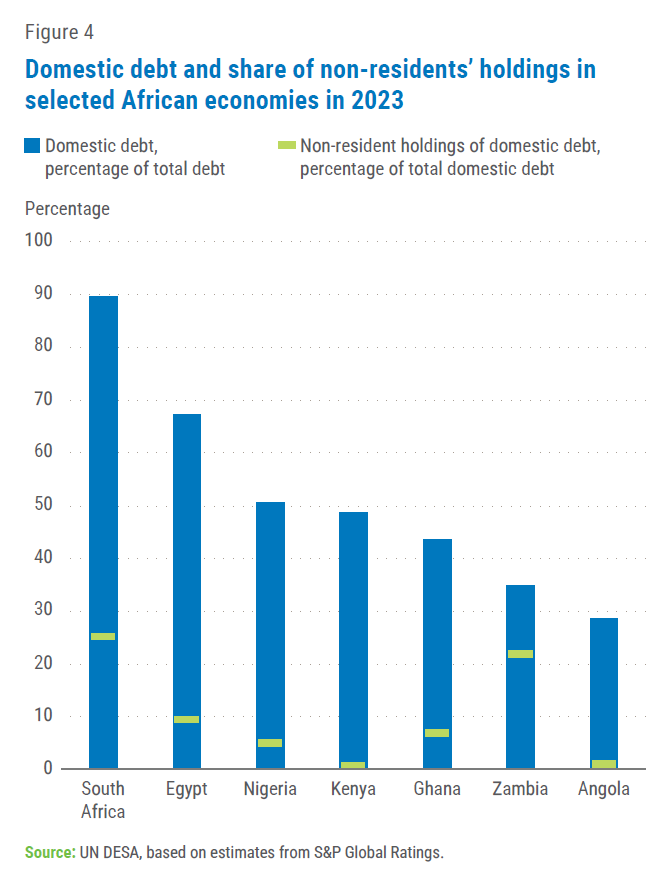 Well-developed domestic public debt markets provide local investors with opportunities to invest in government securities, thus presenting a two-pronged advantage. Firstly, domestic investors are able to participate in the economy while deriving a decent return on their investment, given the relatively low risk of – and attractive interest rates on – government securities. Figure 4 shows domestic debt in selected African countries, illustrating the relatively small non-resident holdings of domestic debt in most countries. Secondly, governments, by sourcing financing from the domestic market, reduce risks of capital outflows. Some countries have measures in place to reduce capital outflow exposure. Zambia, for instance, which as shown in figure 4 has a relatively higher non-residents participation in the domestic debt market, has enacted measures to limit non-residents participation in government bonds primary market to 5 per cent, to lower external pressure on debt sustainability.
Well-developed domestic public debt markets provide local investors with opportunities to invest in government securities, thus presenting a two-pronged advantage. Firstly, domestic investors are able to participate in the economy while deriving a decent return on their investment, given the relatively low risk of – and attractive interest rates on – government securities. Figure 4 shows domestic debt in selected African countries, illustrating the relatively small non-resident holdings of domestic debt in most countries. Secondly, governments, by sourcing financing from the domestic market, reduce risks of capital outflows. Some countries have measures in place to reduce capital outflow exposure. Zambia, for instance, which as shown in figure 4 has a relatively higher non-residents participation in the domestic debt market, has enacted measures to limit non-residents participation in government bonds primary market to 5 per cent, to lower external pressure on debt sustainability.
Domestic debt defaults tend to be rarer than external debt defaults
This could be because policymakers have the option of inflating away domestic debt than recourse to outright default (Herman, Ocampo, and Spiegel, 2012). Also, in countries where domestic financial institutions are the main holders of government domestic debt, effects of a domestic debt default could be severe, and if not properly managed, could result in a widespread financial crisis. In the case of debt default, domestic debt tends to be easier to restructure since it is subject to the jurisdiction of domestic courts. A case study conducted by the IMF on debt restructurings between 1988 and 2020 concluded that domestic debt restructuring took considerably less time to complete compared to external debt restructuring, largely due to a greater sovereign control of the terms and laws governing domestic debt. Additionally, by restructuring domestic debt, countries can avoid the reputational costs associated with external debt restructuring and, in some cases, maintain access to external finance.
Risks associated with domestic debt
Increased reliance on domestic debt, even with the benefits outlined above, carries risks, which if not well managed, could be detrimental to economic growth. One of the key arguments against domestic debt is that it can entail significant crowding-out effects for the domestic private sector. When government is the largest borrower, credit from banking and non-banking financial institutions available to the private sector could diminish (Bua, Pradelli and Presbitero, 2014). Arnone and Presbitero (2010), note that domestic public debt might undermine economic activity through crowding out effects and inflationary pressures if it represents a large share of bank deposits. In Egypt, as of October 2023, domestic public debt was approximately 77 per cent of total domestic credit. In Kenya, as of 2022, exposure of financial institutions to government securities was approximately 40 per cent of the total deposits. As a result, private sector is more credit constrained than the public sector in many African countries. This in turn curtails the private sector’s growth potential since reduced private credit discourages investments into the private sector. Ultimately, crowding out can affect government revenue in the long run if the private sector taxable base grows at a subpar pace, which could in turn hamper the government’s ability to repay its debts. Banks may also find it challenging to adequately diversify their risks, if the high cost of capital leaves a preponderance of more risky projects seeking finance.
Another considerable challenge is the maturity structure of domestic debt instruments. Many developing countries are unable to issue long-term government instruments at reasonable interest rates, in turn issuing mainly short- and medium-term securities (0–9 years). As of 2022, Zambia and Kenya’s domestic debt portfolio comprised of 78.5 per cent and 77.8 per cent of short- and medium-term securities, respectively. The proportion was even higher in Ghana, where short- and medium-term securities accounted for approximately 89.8 per cent of marketable instruments at the end of 2022. This short-term maturity structure increases rollover risks, where governments continually borrow to settle maturing obligations, thus risking macroeconomic instability.
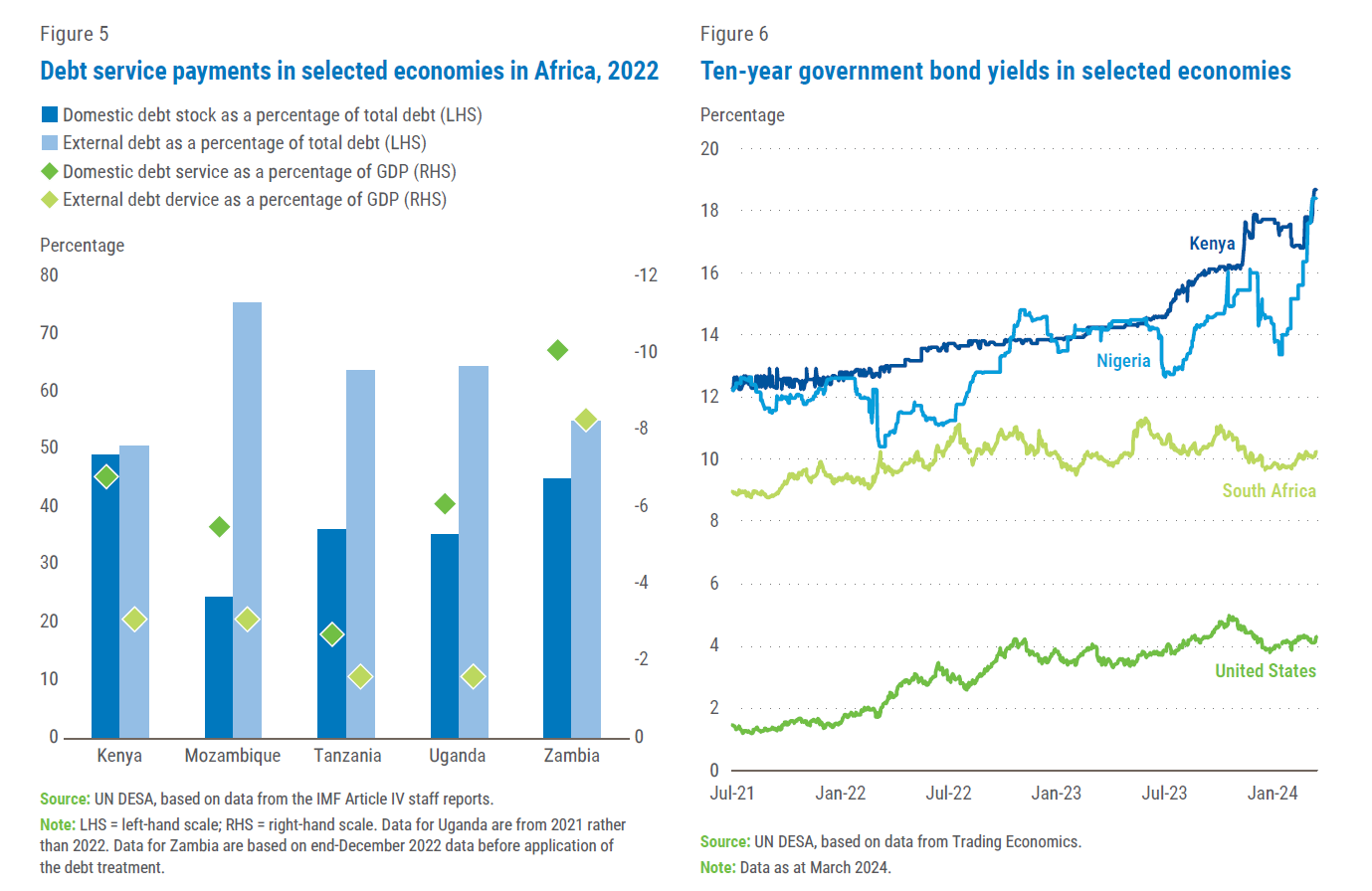
High domestic debt service burdens in some African countries weigh heavily on government finances, further reducing spending which could be directed to investments in critical sectors such as health, education, and infrastructure. Figure 5 compares domestic and external debt service payments in selected African countries in 2022. In this time period, in all the countries below, domestic debt service was higher than external debt service, despite domestic debt stock being lower than external debt stock. Mozambique, for instance, paid 5.5 per cent of GDP in service for domestic debt, which was a quarter of total debt stock, compared to 3.1 per cent of GDP for external debt which made up three quarters of the debt stock. Even more alarming, in 2022, Kenya, Uganda and Zambia spent lower on education than they did on domestic debt service, at approximately 4 per cent, 2.5 per cent and 3.5 per cent of GDP respectively.
In principle, policymakers could lower the cost of domestic debt servicing by inflating away the debt. In such cases, governments may adopt expansionary monetary policies to increase inflation thus effectively lowering the real value of its debt. While this might have some short-term benefits, in the long-term, high inflation may reduce investors’ confidence, increase cost of borrowing through an inflation-risk premium, and affect the long-term performance of the economy.
In some African countries, average real interest rates on domestic debt tend to be higher than nominal interest rate on external debt. This is, however, not always the case because of high inflation in many countries. According to the IMF, the projected average real interest rate on domestic debt for Ghana and Zambia over the period 2023–2032 will be lower than the nominal interest rate on external debt. Figure 6 shows the 10-year Government bond yield in selected countries, with Kenya and Nigeria above 18 per cent as of March 2024. This high yield spread, compared to the US 10-year Government bond yield at 4.21 per cent, illustrates the high-risk perception of many African sovereign debt instruments. Market sentiments, including preference of short-term maturities, as well as a narrow investor base, are some of the factors that could drive up the interest rate on domestic debt.
Implications of domestic debt restructuring on the financial sector and broader economy: Ghana’s experience
Ghana’s debt default (external and domestic) and the subsequent restructuring has put the spotlight on domestic debt in Africa. The country’s public debt has steadily risen in the last decade, from 55.4 per cent of GDP in 2015 to 76.6 per cent in 2021. This trend was driven by Ghana’s access to the international financial markets, having had 15 outstanding Eurobonds at end-2022. In the same time period, domestic debt grew from 22.4 per cent of GDP to approximately 39.6 per cent of GDP mainly because of government borrowing to finance the energy sector and to bail out the finance sector following the 2018–2019 financial crisis. The COVID-19 related expenditure also increased debt by approximately 4.6 per cent of GDP in 2020.
At the time of default in December 2022, total public debt stood at 92.3 per cent of GDP. Some of the factors contributing to the default included an inflated import bill due to effects of the war in Ukraine, drastic depreciation of the cedi and increased cost of debt service. At the same time, external shocks triggered significant capital outflows and diminished access to international financial markets. Moody’s and Fitch downgraded the country’s sovereign credit rating in September 2022, and foreign exchange reserves dwindled to 2.7 months of import cover at end-December 2022, down from 4.3 months at end-December 2021.
In December 2022 the Government initiated a domestic debt exchange programme, aimed at restoring sound public finance management and debt sustainability. Domestic bond holders were offered a chance to exchange their holdings with a fresh issuance of bonds with longer average maturities and lower coupon rates. New bonds were issued at a coupon rate staggered between 0 and 10 per cent. Before the exchange, interest rates for 2–6 years notes ranged between 21.5 per cent and 29.85 per cent. Although the programme managed to lower interest rates on government securities and lengthen their maturities, analysis by the country’s financial sector regulators showed that it adversely affected the solvency of some banks and insurance companies. The Government formed the Ghana Financial Stability Fund to minimize impacts of the restructuring process to the financial sector, and to avoid risks of a potential financial crisis. The IMF demanded satisfactory completion of the domestic debt exchange programme as a prerequisite for continued engagement with external creditors. The restructuring also took a relatively short time, with the domestic debt exchange programme concluding successfully in 2023. In January 2024, Ghana reached an agreement with official creditors under the G20 Common Framework on Debt Treatment.
Some lessons can be derived from Ghana’s experience with the domestic debt restructuring. These include the need to cushion the financial sector from adverse impacts of a domestic debt default. Importantly, countries should also focus on safeguarding vulnerable people by improving social protection in times of economic hardships. In 2023 Ghana doubled benefits distributed through the cash transfer programme targeting people living in poverty. The Government also increased allocations in the education and health sector. Through this experience, Ghana has maintained a growth momentum buttressed by sound financial and monetary policies aimed at restoring macroeconomic stability and debt sustainability. Inflation declined from 54.2 per cent in December 2022 to 23.2 per cent in February 2024. The economy also grew at an average of 2.8 per cent in the first three quarters of 2023, almost double the Government’s initial target of 1.5 per cent GDP growth. In January 2024, the IMF noted that “ambitious structural fiscal reforms are bolstering domestic revenues, improving spending efficiency, strengthening public financial and debt management, preserving financial sector stability, enhancing governance and transparency, and helping create an environment more conducive to private sector investment.”
How can African countries better access and manage their domestic debt?
Domestic debt is a valuable source of finance for African countries. However, it remains a potential source of vulnerability and the consequences of a default on domestic debt can quickly reverberate throughout the economy. The viability of domestic debt will continue to be challenged by short-term maturity preference, limited – or financial sector concentrated – investor base and high interest rates. If these challenges persist, governments will continue to struggle to meet debt repayment obligations and thus worsening debt sustainability.
African countries need to improve macroeconomic policies, debt management and regulatory frameworks to ensure long term sustainability of domestic debt. Firstly, a stable macroeconomic environment, especially a low and stable inflation rate, is necessary to build investor confidence and appetite in medium- and long-term government debt instruments. In addition, a broad investor base, including non-financial institutional investors is also required to reduce the risk of a private credit crunch caused by overexposure of financial institutions to government lending. This will also accelerate development of domestic bond markets, in turn improving resilience to global shocks by reducing reliance on external borrowing. Finally, and most importantly, proceeds from debt must be used productively – by investing in projects with high economic returns – to ensure governments’ ability to sustainably service their debt obligations.
Going forward, as African governments continue to seek an optimal debt structure, they will need to strengthen their debt sustainability frameworks to adequately balance the trade-offs associated with domestic debt. Lack of timely action on this will only exacerbate existing debt vulnerabilities, which could negate development progress and put the SDGs even further out of reach for countries most in need.

Follow Us