Every day, people are dying from infections that cannot be treated anymore. Our misuse and overuse of antibiotics and other antimicrobials has led to an increase in microbes that are resistant to the medicines designed to kill them.
Health
Nuclear-derived tools supplied by IAEA in partnership with FAO play a critical role in researching, detecting, diagnosing and characterizing zoonotic diseases such as COVID-19. In recent discoveries, COVID-19 infections have been recorded to transmit from humans to minks and back to humans, showing that the virus quickly adapts to new hosts. Understanding such mutations is vital in the development of effective vaccines.
WHO‘s Global Strategy to Accelerate the Elimination of Cervical Cancer outlines three key steps: vaccination, screening and treatment. Successful implementation could reduce more than 40% of new cases of the disease and 5 million related deaths by 2050. This historic milestone marks the first time that 194 countries commit to eliminating cancer - following adoption of a resolution at this year’s World Health Assembly.
In Palestine, it is widely understood that vulnerability to breast cancer can be hereditary. As a result, some women avoid getting screened because they fear a breast cancer diagnosis could affect their daughters’ marriage prospects. Women with breast cancer have also faced gender-based violence and abandonment. A recent UNFPA study showed that breast cancer stigma is a major cause of delayed detection and treatment.
World Antimicrobial Awareness Week (WAAW) aims to increase awareness of global antimicrobial resistance and to encourage best practices among the general public, health workers and policy makers to avoid the further emergence and spread of drug-resistant infections. FAO, WHO and partners, expanded the scope of the Observance, changing its focus from "antibiotics" to the more encompassing and inclusive term "antimicrobials". The week will be celebrated every year on 18-24 November starting from 2020. This year’s theme for the human health sector is “United to preserve antimicrobials".
One stillbirth happens every 16 seconds. That’s about 2 million babies stillborn every year. What makes these deaths even more tragic is that the majority could have been prevented through quality care during pregnancy and at birth. Beyond the devastating loss of life, the psychological and financial costs for women, families and societies are severe and long lasting. Here are the answers to key questions about stillbirths.
More than half of all road traffic deaths are among vulnerable road users: pedestrians, cyclists, and motorcyclists. A higher proportion of vulnerable road users die in low-income countries than in high-income countries. The World Day of Remembrance for Road Traffic Victims has become an important tool in global efforts to reduce road casualties. It offers an opportunity for drawing attention to the scale of emotional and economic devastation caused by road crashes and for giving recognition to the suffering of road crash victims and the work of support and rescue services.
Diabetes is a major cause of blindness, kidney failure, heart attack, stroke and lower limb amputation. The UN encourages the development national policies for the prevention, treatment and care of diabetes in line with the sustainable development of their health-care systems. Over the past decade, diabetes prevalence has risen faster in low and middle-income countries than in high-income countries. This year’s World Diabetes Day (14 Nov) focuses on the nurse and diabetes. The campaign aims to raise awareness around the crucial role that nurses play in supporting people living with diabetes.
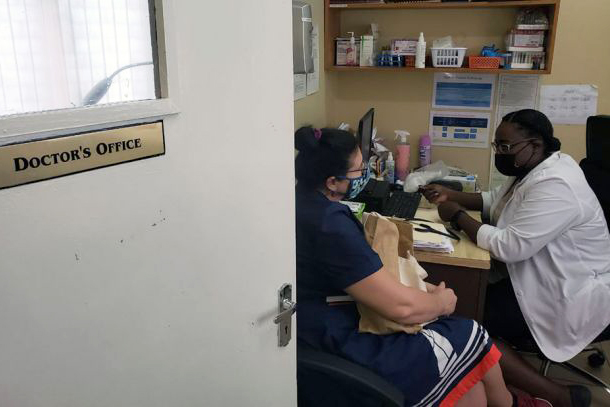
HIV service providers in Jamaica have been challenged this year with responding both to new challenges caused by COVID-19 and long-standing service delivery stumbling blocks. CHARES had been used to writing three-month prescriptions for stable clients, but since COVID-19, state-run pharmacies have been dispensing only a one-month supply. The Comprehensive Health Centre serves a number of people living with HIV alongside those infected with other sexually transmitted infections. Here, too, multimonth dispensing has not been possible during COVID-19.
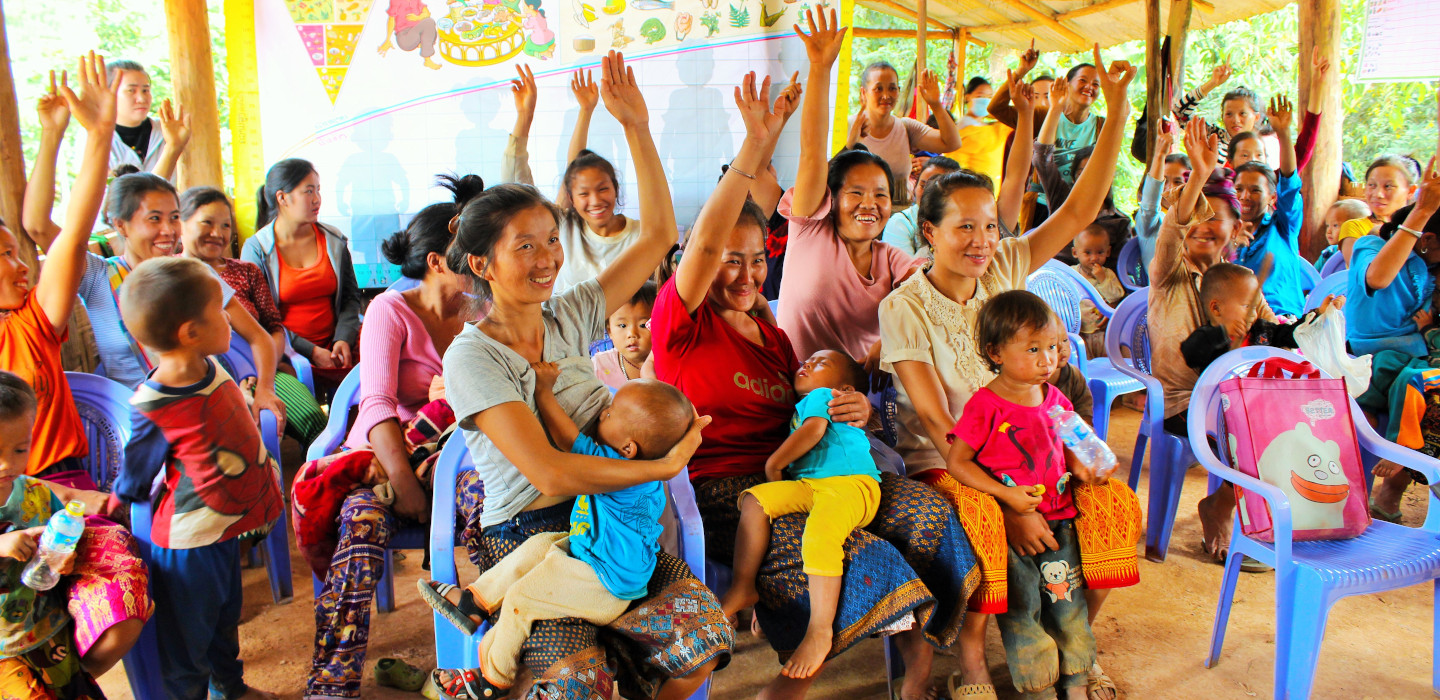
In this month’s programme, we have the latest on COVID-19 from IFAD’s Associate Vice-President Donal Brown; news on nutrition from the Lao People’s Democratic Republic; and a report on getting youth issues right in development activities. We also speak with Marco Minciaroni, a leader in Italy’s agro-ecological movement.
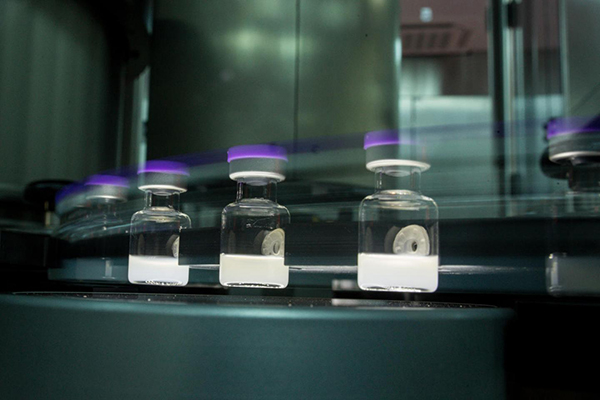
A vaccine for COVID-19 will be a critical tool for helping bring the pandemic under control when combined with effective testing and existing prevention measures. Experts around the world are working hard to accelerate the development and manufacturing of a safe and effective vaccine. Here are answers to some of the most common questions: When will a COVID-19 vaccine be ready? How is the COVID-19 vaccine being developed? Will a coronavirus vaccine be safe? Get the answers to these and more.
UNDP launches a global campaign to end poverty and raise awareness of the alarming rate at which COVID-19 and climate change are increasing inequalities around the world.
While recent data collection has shown that the COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on HIV testing services, the impact on HIV treatment is less than originally feared. In a study conducted by UNAIDS, World Health Organization and United Nations Children's Fund, only five out of 22 countries reported monthly declines in the number of people on treatment after April—these include Zimbabwe in June, Peru and Guyana in July, the Dominican Republic in April, and Sierra Leone in May through to July. The remaining 18 countries did not show a decline and some countries showed a steady increase (e.g. Kenya, Ukraine, Togo and Tajikistan).
The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted or halted critical mental health services in 93% of countries worldwide while the demand for mental health is increasing. A recent WHO survey of 130 countries provides the first global data showing the devastating impact of COVID-19 on access to mental health services and underscores the urgent need for increased funding. Prior to the pandemic, countries were spending less than 2 per cent of their national health budgets on mental health and the pandemic is increasing demand for mental health services.