
The Global Dividend for Maximum Impact (GDM-I):Advancing Women for Global Equity and Innovation
Developing countries and vulnerable communities must shift away from a classic development model to one that creates an enabling environment, not only to solve domestic challenges of inequity and social injustice, but to establish truly multilateral and mutually beneficial relationships to address pressing global issues, secure competitive advantages, and build stable economies. In other words, just like established and emerging economies, developing nations must create an infrastructure for ensuring sustainability. To do this, they need partnerships for quality higher education, advanced research, and an integrated innovations agenda.

A Quiet Diplomat for Challenging Times
Which Ban Ki-moon -- the criticized early version, or the latest, emboldened edition -- will be seen during his second term leading the world body in pursuit of international peace and security? Although an in-depth treatment is beyond the scope of this article, in the hope of stimulating further analysis a few words can be said on the pivotal functions of the Secretary-General. In the area of peace and security, the Secretary-General wears several hats: he is the general of peacekeeping, the political prince of world diplomacy, the secular pope of the values of the Charter, and the global CEO of a complex, international bureaucracy. All of these roles are intertwined and complementary, but for the sake of analytical clarity, this article addresses each one separately.

Improving UN Responses to Humanitarian Crises
In the aftermath of the Second World War, the creation of the United Nations and documents such as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the Genocide Convention, the four Geneva Conventions of 1949, and their Additional Protocols, as well as concepts such as responsibility to protect (R2P), have transformed international law and the basis for how states must conduct international relations. Yet, as David Rieff, who has covered several wars and humanitarian emergencies, remarks in his book A Bed for the Night: Humanitarianism in Crisis, the murderous twentieth century remained just as murderous.
The Dilemma of Democratization in Fragile States
Conventional thinking juxtaposes democracy and dictatorship as mutually exclusive systems. It is often assumed that when one system collapses, it is replaced by the other, as if this was the natural order of things. Some theorists, such as Francis Fukuyama, argued that liberal democracy had decisively defeated tyranny with the collapse of the Soviet Union, which marked the end of history. Indeed, since then, while there have been setbacks in countries such as Ukraine and Zimbabwe, dictatorship has been in retreat.

The UN Role and Efforts in Combating the Proliferation of Small Arms and Light Weapons
The proliferation of small arms and light weapons (SALW) in various parts of the globe continues to pose a systemic and pervasive threat to the long-term social and economic development of many nations, particularly in small developing states.
If You Want the Peace of the Dead, Prepare for Nuclear War
Nuclear weapons are strategic equalizers for weaker sides in conflict relationships, but they do not buy defence on the cheap. They can lead to the creation of a national security state with a premium on governmental secretiveness, reduced public account- ability, and increased distance between citizens and Governments. There is the added risk of proliferation to extremist elements through leakage, theft, state collapse, and state capture. In terms of opportunity costs, heavy military expenditure amounts to stealing from the poor. Nuclear weapons do not help to combat today's real threats of insurgency, terrorism, poverty, illiteracy, malnutrition and corruption. As they said in the streets of Delhi in 1998: No food, no clothing, no shelter? No worry, we have the bomb.
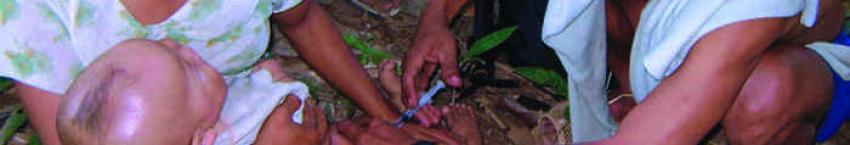
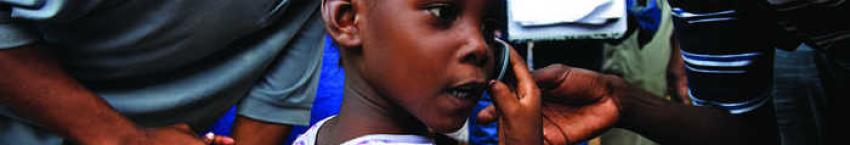
Advancing the Global Health Agenda
The global health agenda brings together two critical action spheres of our time: managing interdependence and globalization, and addressing the growing inequalities within and between nations through development strategies. It also lies at the intersection of many policy arenas and is subject to a special dynamic. On the one hand, poor health is frequently a consequence of other global crises such as finance, food insecurity, or climate change, while on the other hand, the whole of society bears the impact if health challenges are not well managed.
Sustainability Agenda in Retrospect and in Prospect
Since the adoption of Agenda 21 in 1992, the United Nations has been pursuing sustainable development in the economic, social, and environmental fields, and at the local, national, and international levels. Due to efforts of the past two decades, the United Nations has been successful in spreading the concept of sustainable development far and wide, carrying out various forms of relevant activities on a regular basis, and establishing numerous international political commitments. As countries become increasingly interdependent, the desire for sustainable development has become stronger in a concerted way. It would be fair to say that an era of sustainable development is being ushered in right now.
Strengthening Crisis Information Management
Recognizing the potential for both good and bad uses of the Internet, ICT4Peace aims to facilitate improved, effective, and sustained communication between peoples, communities, and stakeholders involved in conflict prevention, mediation, and peace building through better understanding and enhanced application of ICT, including media.

Dag Hammarskjöld Stood Up for the UN on Development
Freedom and prosperity must come to Africa from within. Let us pray that it will not resort to quick fixes, revenge, violence, and wars that have kept it down for so many years.

Digital Asia-Pacific in the Twenty-First Century
Change is accelerating in the Asia-Pacific region, including in rural areas, as it becomes the global economy's growth driver. In 2010, the region's developing countries grew at an impressive rate of 8.8 per cent compared to 2.7 per cent for the world's developed economies.

Context and Design in ICT for Global Development
Information and communication technology is deeply woven into the fabric of society and is integral to the way we do business, entertain ourselves, talk to each other, learn about the world, and even feed ourselves. With nearly five billion mobile phones worldwide, the reach of ICTs is increasingly global. However, even with this near ubiquity, the benefits of ICTs remain uneven -- access to the world information society does not immediately grant membership.

The ICT/Poverty Nexus
Despite the persistence of widespread poverty, the use of mobile telephony in African countries in the last few years has grown more rapidly than in any other region in the world. There are now an estimated 500 million mobile phone subscribers across the continent compared to 246 million in 2008. By late 2010, Africa exceeded Western Europe in terms of the number of mobile connections.
Rewarding Scientific Knowledge for Sustainable Development
Sustainable development is a critical issue in the management of global survival and environmental preservation. Increasingly, it is extending its reach across a broad multidisciplinary policy canvas, impacting on economic, social and cultural spheres aimed at securing an improved quality of life for the international community.

Bridging the Digital Divide in Health
A fundamental change in the years since the MDGs were agreed upon is the appreciation of the role that ICT can play in meeting health targets. It was not so long ago that health decision makers were questioning the utility of adopting ICT in health services and systems -- that is, e-Health -- particularly in developing countries.
