Find out more in
Global Issues
Did you know that you can save three lives in just ten minutes with the gift of your blood? What do countries need to do to have safe blood donation systems ? WHO’s Dr. Yuyun Maryuningsih explains all you need to know to donate blood in Science in 5.
Leaders from around the world meeting at the 80th Session of the UN General Assembly have adopted a political declaration to combat noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) and mental health challenges through a fully integrated approach. The document is the first such declaration addressing NCDs and mental health together, and marks a unique opportunity to accelerate global progress with a set of specific global targets for 2030. Mental health is increasingly recognized as a universal human right and an essential foundation of human development. Learn more about mental health and how to sustain it.
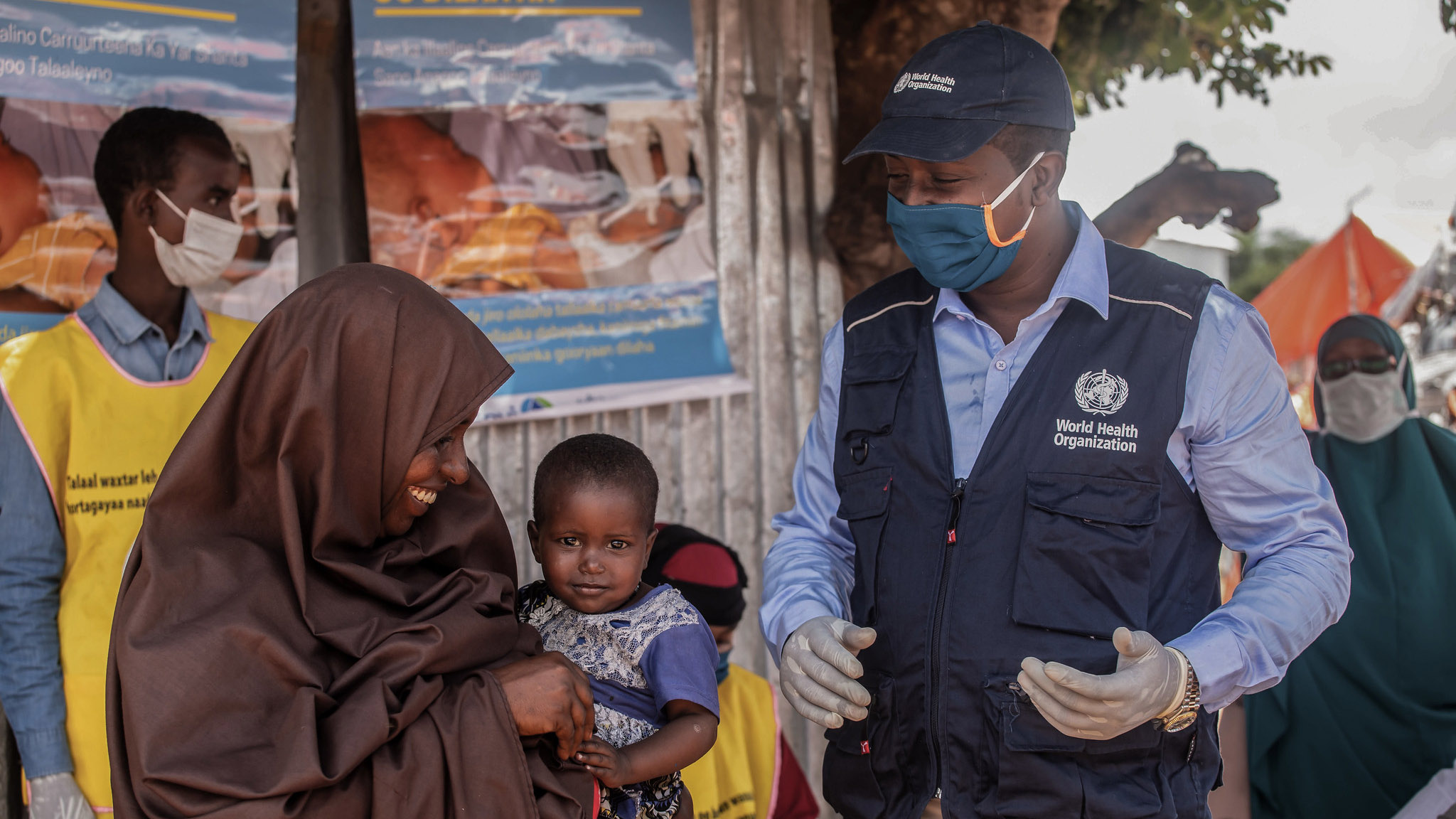
Resilient communities are fundamental to preventing, and responding to, epidemics and pandemics. Our best defense lies not only in science, but also in strong local health systems, well-supported frontline health workers, and local leaders who are prepared to guide their communities through crisis. This International Day of Epidemic Preparedness (27 December) let’s help all communities build a strong foundation for both prevention and recovery. Let’s stop epidemics in their tracks.
Since 2000, nations have advanced toward universal health coverage, more care, and less financial strain. Yet billions still lack essential services, and millions are pushed deeper into poverty by out-of-pocket costs, largely for medicines. A new study from the World Health Organization-World Bank warns: without bold investment, by 2030 many will still face hardship. Health is a right, but for too many, it remains a distant promise.
Meditation, an ancient practice rooted in diverse traditions, focuses attention on the present to promote mental clarity, emotional calmness, and physical relaxation. Today, it’s a global tool for well-being, reducing stress and anxiety, and improving sleep and physical health. The World Health Organization (WHO) endorses mindfulness meditation for mental health and highlights yoga’s benefits, while technology broadens access via apps. Recognizing its universal value, the United Nations declared 21 December World Meditation Day to promote health and collective well-being.
More than half of the world’s population still lacks access to essential health services. And a quarter of them face financial hardship when paying for health care out of their own pockets, often at the expense of food, education or housing. International Universal Health Coverage Day (12 December) is the annual rallying point for the global movement for health for all. Building on momentum from 2024, this year's campaign highlights the devastating human impact of unaffordable health costs and calls on decision-makers to prioritize universal health coverage.
In 2025, a historic funding crisis is threatening to unravel decades of progress in HIV prevention. AIDS is not over and given today’s environment, a new transformative approach is needed to mitigate risks and help reach the targets. Countries must make radical shifts to HIV programming and funding. The global HIV response cannot rely on domestic resources alone. This World AIDS Day (1 December), join us in calling for sustained political leadership, international cooperation, and human-rights-centred approaches to end AIDS by 2030.
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) makes infections harder to treat, and World AMR Awareness Week, held every November 18–24, raises global awareness and drives action to combat this growing health threat.
A worm that can cause epilepsy? Meet Taenia solium — the pig tapeworm that travels from gut to brain, causing seizures and preventable epilepsy in millions. In this episode of WHO' Science in 5, Dr Bernadette Abela explains how this parasite spreads when pigs eat human feces and humans consume contaminated food or water — and what we can do to stop it. Learn how cooking meat properly, improving hygiene, and vaccinating pigs can break the cycle.
Conjoined twins are a rare type of identical twins that share a placenta and an amniotic sac. The estimated incidence of this condition can be 1 in 50,000 births. On the World Conjoined Twins Day (24 November) we emphasize the need to address the condition of conjoined twins by raising awareness of their cases at all levels and through a life-course approach, as well as by advocating for their well-being and social inclusion, while taking into account relevant agreed international standards, norms and principles.
With a global shortage of 900,000 midwives, training the next generation of these crucial health workers, to avoid preventable deaths and ensure safe births, is a priority for UNFPA, the United Nations sexual and reproductive health agency. The training school in Abidjan is one of eight schools UNFPA supports in the country. Models of pregnant women and babies are used to simulate childbirth, including emergency deliveries, in a safe, realistic and risk-free environment – because in real life, there is no test run. In Côte d’Ivoire, many women give birth without the assistance of a skilled health professional. With the support of UNFPA, the National Institute for the Training of Health Workers is working to change this, and also tackling the country’s high rates of maternal mortality and adolescent pregnancy and low contraceptive prevalence.
As a result of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), antibiotics and other antimicrobial agents become ineffective, making infections difficult or impossible to treat, increasing the risk of disease spread, severe illness and death.& The World AMR Awareness Week (18-24 November) is a global campaign to promote global action to tackle the emergence and spread of drug-resistant pathogens. This year's theme “Act Now: Protect Our Present, Secure Our Future” underscores the urgent need to take bold, united action to address AMR, which is already harming our health, food systems, environment and economies.
Every year, millions more road victims are added to the current toll of over 50 million killed and hundreds of millions injured since the first road death. When people are killed or severely injured in road traffic collisions, the world loses more than just individuals — it loses potential, ideas and future impact on society. They become lost talents. On World Day of Remembrance for Road Traffic Victims (16 November) we encourage all road safety stakeholders to honor those who have died on the world’s roads, advocate for better support for victims and bereaved families and promote action to save lives.
In 2025, after a decades-long fight against malaria, Suriname was certified as malaria-free by the World Health Organization. Hear the voices from the front lines.