UN DESA | DPAD | Development Policy Analysis Division
Capacity Development and Advisory Services
Millennium Development Goals
Tunisia highlights
Tunisia's progress towards the MDGs has been uneven
 |
Tunisia will likely achieve many of the MDGs given the progress it made before the recent revolution. The country cannot become complacent, though; serious gaps remain, particularly in lowering the maternal mortality rate and providing more access to basic sanitation. To close these gaps and also meet targets for primary education, child mortality and access to drinking water, the Government would have to raise spending by 5-6% of GDP. Meeting the target for maternal mortality would be the most expensive.
Domestic resource mobilization to finance the MDGs
may not be a feasible option
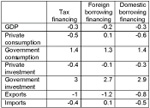
| Macroeconomic indicators in alternative MDG-financing scenarios, 2006-2015 |
 |
| Hover to expand |
Injection of additional financing to achieve the development goals can have various macroeconomic consequences in Tunisia, depending on the source of funding. Domestic borrowing and increased taxation are likely to crowd-out domestic consumption and investments, which, in turn, would slow the growth of economic activity. In any case, resource mobilization through domestic savings may not be an option given the likely negative economic impact of the recent revolution and declining workers' remittances on household incomes.
In Tunisia, foreign aid seems crucial for achieving
development goals
| Foreign aid requirements to finance the cost of the MDGs, 2011-2015 |
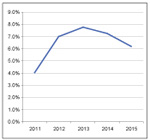 |
In reaction to the recent political changes and constitutional amendments, the international donor community has pledged financial support to Tunisia. The country does indeed need foreign aid to reconstruct its political system, spur economic growth and finance development goals. It is estimated that, on average, a minimum increase of 6% of GDP per year in foreign aid would be needed to finance key development goals.
Related documents
- Country study "Assessing Development Strategies to Achieve the MDGs in the Republic of Egypt" (2011).
- Country study "Assessing Development Strategies to Achieve the MDGs in the Republic of Morocco" (2011).
- Country study "Assessing Development Strategies to Achieve the MDGs in the Republic of Yemen" (2011).