Document_GEM: UN DESA Policy Briefs series
UN DESA Policy Briefs series
1 April 2020
Countries are quickly acting to counter its negative impact on employment and poverty, including through fiscal stimulus plans. Whether these plans will protect the most disadvantaged people and households over the long-term depends on their size, duration and on how measures are implemented.
14 March 2018
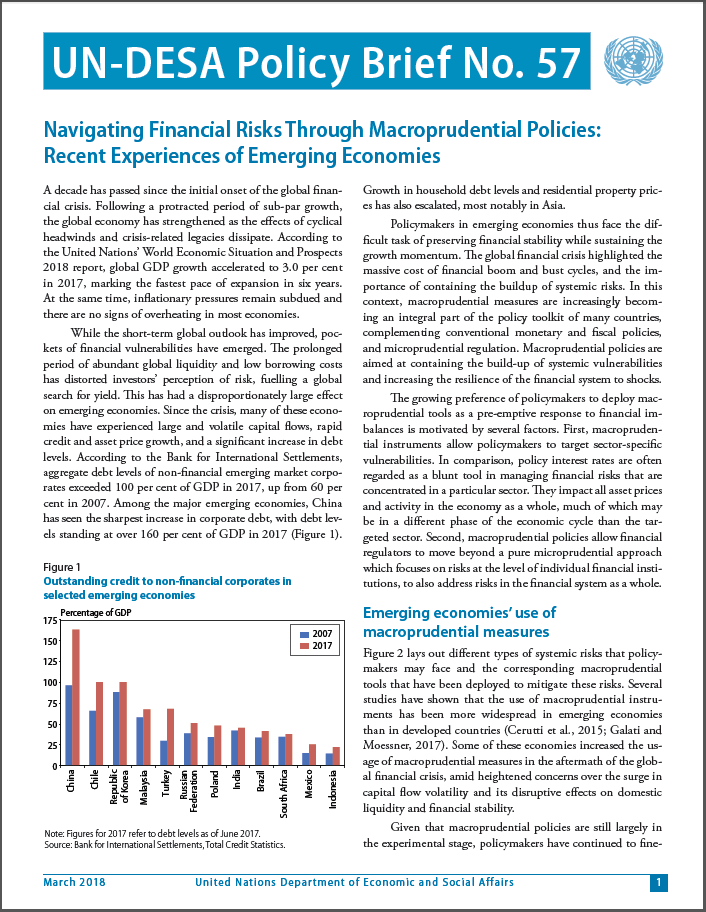
A decade has passed since the initial onset of the global financial crisis. Following a protracted period of sub-par growth, the global economy has strengthened as the effects of cyclical headwinds and crisis-related legacies dissipate.
1 September 2017
The WESS has been the earliest and continuous post-World War II development-focused report, predating any other world development report that appeared thereafter. It was born as a response to the resolution 118 (II) of 31 October 1947.
27 August 2017
Globalization and technological progress have enabled unprecedented gains in wellbeing across the world. However, imbalances in global flows, when they emerge, continue to plague the global economic and financial system, and cause development setbacks. The turbulence of the last decade demonstrated once again that global mechanisms remain ill-suited to protect the most vulnerable countries and populations groups from the effects of crises.
26 August 2017
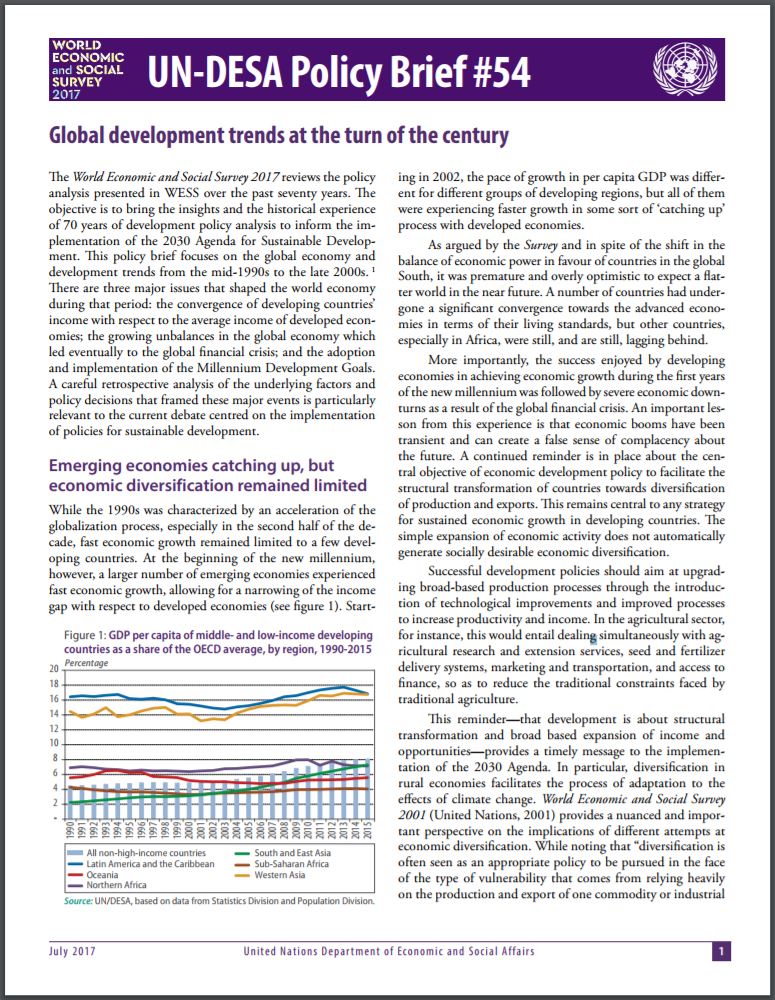
From the mid-1990s to the late 2000s, there are three major issues that shaped the world economy: the convergence of developing countries’ income with respect to the average income of developed economies; the growing unbalances in the global economy which led eventually to the global financial crisis; and the adoption and implementation of the Millennium Development Goals.
25 August 2017
After almost three decades of remarkable progress since the end of the Second World War, economic conditions started to deteriorate in the 1970s. Economic growth slowed down in all parts of the world during the second half of the 1970s and the first half of the 1980s. Before the oil price shock of 1973, the annual growth of world gross product had been at 5.3 per cent, while during the rest of the 1970s, annual world growth reached only 2.8 per cent.
23 August 2017
The Golden Age of Capitalism spanned from the end of the Second World War in 1945 to the early 1970s, when the Bretton Woods monetary system collapsed. It was a period of economic prosperity with the achievement of high and sustained levels of economic and productivity growth. During the Golden Age, the themes taken up by World Economic and Social Survey, henceforth referred to as the Survey, varied from year to year, in response to pressing development concerns.
20 July 2017
In drawing the most relevant lessons for implementing the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the World Economic and Social Survey 2017 systematically reviews the seven decades of development discussions contained in the publication – the oldest continuous publication of its kind.
3 September 2016
In the past 20 years, weather-related disasters affected 4.2 billion people worldwide, with a large loss of life and livelihoods. The global annual average cost of climatic disasters, including floods, storms, droughts and heat waves, is estimated to h ...









Follow Us